Medical Ozone as a Therapeutic Option in Musculoskeletal Pain Control: A Critical Review of Clinical Trials Considering Safety and Quality Indicators for Procedures and Devices
- PMID: 39351322
- PMCID: PMC11426297
- DOI: 10.59249/HGTG9363
Medical Ozone as a Therapeutic Option in Musculoskeletal Pain Control: A Critical Review of Clinical Trials Considering Safety and Quality Indicators for Procedures and Devices
Abstract
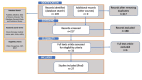
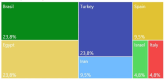
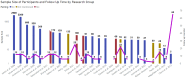
Background: Drug therapies have been widely applied for pain management, however, there are important side effects such as those related to corticosteroids and opioids. Recent studies demonstrated promising results using medical ozone as a safe, effective, and low-cost intervention for pain control. Objective: to review and critically analyze clinical studies that used ozone therapy for musculoskeletal pain. Methods: a literature search of various databases was performed to identify relevant studies. From a total of 249 records, 27 studies were included. Quality indicators, human and device factors that strongly influence the generation of evidence were considered, such as study design and device safety. We also mitigated biases, considering the safety and efficacy of the intervention itself. Results: Regarding safety, 77 (8%) of studies reported no adverse effects; concerning efficacy outcomes, medical ozone shows to be an effective intervention on musculoskeletal pain control. Important information about used devices were missing. Conclusions: medical ozone shows to be safe and effective; qualification of health professionals as well as the device safety are mandatory. However, there is a lack of requirements to identify the best therapeutic scheme; further longer, clinical and rigorous trials are needed.
Keywords: clinical trials; evidence; medical ozone; ozone therapy; pain.
Copyright ©2024, Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Bocci VA. Ozone: A New Medical Drug. Italy: Springer; 2011. p. 295. 10.1007/978-90-481-9234-2 - DOI
-
- Sánchez GM. Challenges of ozone therapy and access to information sources. Rev Cuba Farm. 2014;48:347–9.
-
- Zhang W, Fei W, Zhang L, et al. Intrathecal injection of ozone alleviates CCI-induced neuropathic pain via GluR6-NF-kB/p65 signalling pathway in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2020;•••:231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
