A bioengineered tumor matrix-based scaffold for the evaluation of melatonin efficacy on head and neck squamous cancer stem cells
- PMID: 39351489
- PMCID: PMC11440243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101246
A bioengineered tumor matrix-based scaffold for the evaluation of melatonin efficacy on head and neck squamous cancer stem cells
Abstract
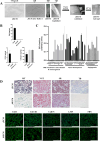
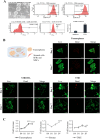
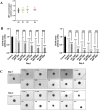
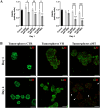
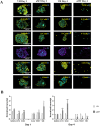
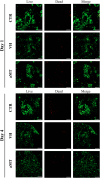
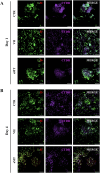
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) presents a significant challenge worldwide due to its aggressiveness and high recurrence rates post-treatment, often linked to cancer stem cells (CSCs). Melatonin shows promise as a potent tumor suppressor; however, the effects of melatonin on CSCs remain unclear, and the development of models that closely resemble tumor heterogeneity could help to better understand the effects of this molecule. This study developed a tumor scaffold based on patient fibroblast-derived decellularized extracellular matrix that mimics the HNSCC microenvironment. Our study investigates the antitumoral effects of melatonin within this context. We validated its strong antiproliferative effect on HNSCC CSCs and the reduction of tumor invasion and migration markers, even in a strongly chemoprotective environment, as it is required to increase the minimum doses necessary to impact tumor viability compared to the non-scaffolded tumorspheres culture. Moreover, melatonin exhibited no cytotoxic effects on healthy cells co-cultured in the tumor hydrogel. This scaffold-based platform allows an in vitro study closer to HNSCC tumor reality, including CSCs, stromal component, and a biomimetic matrix, providing a new valuable research tool in precision oncology.
Keywords: 3D hydrogel; 3D scaffold; Cancer stem cells; Decellularized extracellular matrix; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Melatonin; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Florido J., Martinez-Ruiz L., Rodriguez-Santana C., López-Rodríguez A., Hidalgo-Gutiérrez A., Cottet-Rousselle C., Lamarche F., Schlattner U., Guerra-Librero A., Aranda-Martínez P., Acuña-Castroviejo D., López L.C., Escames G. Melatonin drives apoptosis in head and neck cancer by increasing mitochondrial ROS generated via reverse electron transport. J. Pineal Res. 2022;73 doi: 10.1111/JPI.12824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Ruiz L., Florido J., Rodriguez-Santana C., López-Rodríguez A., Guerra-Librero A., Fernández-Gil B.I., García-Tárraga P., Garcia-Verdugo J.M., Oppel F., Sudhoff H., Sánchez-Porras D., Ten-Steve A., Fernández-Martínez J., González-García P., Rusanova I., Acuña-Castroviejo D., Carriel V.S., Escames G. Intratumoral injection of melatonin enhances tumor regression in cell line-derived and patient-derived xenografts of head and neck cancer by increasing mitochondrial oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023;167 doi: 10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2023.115518. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

