A systematic PCR record-based re-call of HCV-RNA-positive people enables re-linkage to care and HCV elimination in Austria - The ELIMINATE project
- PMID: 39351692
- PMCID: PMC11586887
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.16076
A systematic PCR record-based re-call of HCV-RNA-positive people enables re-linkage to care and HCV elimination in Austria - The ELIMINATE project
Abstract
Background and aims: Identification of people living with hepatitis C virus (HCV) via readily available laboratory records could be a key strategy for macro-elimination, aligning with the WHO elimination goal. Therefore, the ELIMINATE(ELIMINation of HCV in AusTria East) project aimed to systematically re-link people with a 'last-positive' HCV-RNA PCR record to care.
Methods: In 10 major liver centres in Eastern Austria, a systematic readout of 'last-positive' HCV-RNA PCR test records obtained between 2008 and 2020 were conducted and linked to available patient contact data. Between 2020 and 2023, individuals were contacted first by phone, then by letter, to inform them about the availability of effective direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment and invite them for pre-treatment evaluation.
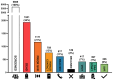
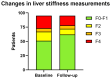
Results: The overall cohort of last-positive HCV+ individuals included 5695 subjects (62.5% males, mean age 57.3 ± 17.3 years); of note, 1931 (34%) of them had died and 759 (13%) individuals had no valid contact information. Of the remaining 3005 individuals, 1171 (40.0%) had already achieved sustained virological response (SVR) at the time of re-call. We successfully reached 617 (20.5%), of whom 417 (67.6%) attended their pre-treatment visit, and 397 (64.3%) commenced DAA-therapy. HCV cure has been confirmed in 326 individuals, corresponding to an SVR rate of 82.1%.
Conclusion: The ELIMINATE project identified 5695 people living with HCV who were 'lost to care' despite documented HCV viraemia. While invalid contact data were an evident barrier to HCV elimination, premature deaths among the cohort underscored the severity of untreated HCV. The implementation of a systematic HCV-RNA PCR recorded-based re-call workflow represents an effective strategy supporting the WHO goal of HCV elimination.
Keywords: DAA; WHO; elimination; hepatitis C.
© 2024 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose regarding the work under consideration for publication. L.D., M.J., L.H., L.W., N.P., B.H., A.S., R.S., A.V.‐G., W.H., M.W., K.K., S.J.‐S., S.T., W.K., C.M., L.A., L.Bu., G.W., F.R., H.L., J.H., C.W., J.W.‐W., P.W., M.N., D.S., J.R. and S.R. have nothing to disclose outside of the submitted work. L.B. received speaking honoraria from Chiesi and Gilead. M.S. received travel support from MSD, Sandoz, BMS, AbbVie and Gilead; and speaking honoraria from BMS. D.C. served as a speaker and/or advisory board member for Gilead, ViiV Healthcare and MSD and received travel support from MSD, ViiV Healthcare and Gilead. M.M. served as a speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Collective Acumen, Echosens, Gilead, Takeda and W. L. Gore & Associates and received travel support from AbbVie and Gilead. M.G. received grant support from AbbVie, Gilead and MSD; speaking honoraria from AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Intercept and MSD; consulting/advisory board fees from AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Intercept, Norgine, AstraZeneca, Falk, Shionogi and MSD; and travel support from AbbVie and Gilead. A.M. received grant support from AbbVie and Gilead; speaking honoraria from AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Intercept, and MSD; consulting/advisory board fees from AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Intercept, Norgine and MSD; and travel support from AbbVie, Gilead and Roche. T.R. served as a speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member speaking honoraria from AbbVie, Bayer, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Roche, Siemens and W. L. Gore & Associates and received travel support from AbbVie, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Gilead and Roche as well as grants/research support from AbbVie, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Gilead, Intercept, MSD, Myr Pharmaceuticals, Philips Healthcare, Pliant, Siemens and W. L. Gore & Associates. D.B. received travel support from Gilead and AbbVie; speaking honoraria from AbbVie and Siemens and grant support from Gilead and AbbVie. C.S. received travel support from Gilead, AbbVie, Galápagos and Gebro; speaking honoraria from AbbVie and Gilead; and payments for consulting from Gilead.
Figures


References
-
- EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: final update of the series. J Hepatol. 2020;73(5):1170‐1218. - PubMed
-
- Westbrook RH, Dusheiko G. Natural history of hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2014;61(1 Suppl):S58‐S68. - PubMed
-
- Martinello M, Solomon SS, Terrault NA, Dore GJ. Hepatitis C. Lancet. 2023;402(10407):1085‐1096. - PubMed
-
- Lawitz E, Mangia A, Wyles D, et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(20):1878‐1887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

