A comprehensive numerical procedure for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of breast tumour on an anatomically realistic breast phantom
- PMID: 39352893
- PMCID: PMC11444401
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310899
A comprehensive numerical procedure for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of breast tumour on an anatomically realistic breast phantom
Abstract
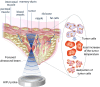
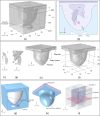
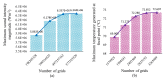
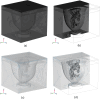
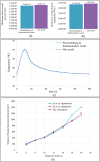
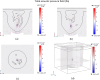
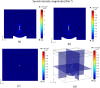
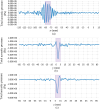
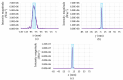
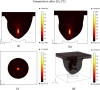
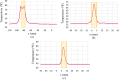
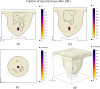
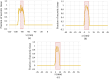
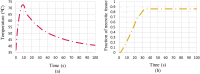
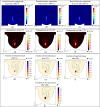
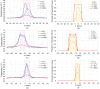
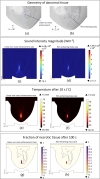
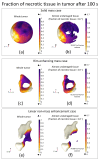
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) as a promising and impactful modality for breast tumor ablation, entails the precise focalization of high-intensity ultrasonic waves onto the tumor site, culminating in the generation of extreme heat, thus ablation of malignant tissues. In this paper, a comprehensive three-dimensional (3D) Finite Element Method (FEM)-based numerical procedure is introduced, which provides exceptional capacity for simulating the intricate multiphysics phenomena associated with HIFU. Furthermore, the application of numerical procedures to an anatomically realistic breast phantom (ARBP) has not been explored before. The integrity of the present numerical procedure has been established through rigorous validation, incorporating comparative assessments with previous two-dimensional (2D) simulations and empirical data. For ARBP ablation, the administration of a 0.1 MPa pressure input pulse at a frequency of 1.5 MHz, sustained at the focal point for 10 seconds, manifests an ensuing temperature elevation to 80°C. It is noteworthy that, in contrast, the prior 2D simulation using a 2D phantom geometry reached just 72°C temperature under the identical treatment regimen, underscoring the insufficiency of 2D models, ascribed to their inherent limitations in spatially representing acoustic energy, which compromises their overall effectiveness. To underscore the versatility of this numerical platform, a simulation of a more clinically relevant HIFU therapy procedure has been conducted. This scenario involves the repositioning of the ultrasound focal point to three separate lesions, each spaced at 3 mm intervals, with ultrasound exposure durations of 6 seconds each and a 5-second interval for movement between focal points. This approach resulted in a more uniform high-temperature distribution at different areas of the tumour, leading to the ablation of almost all parts of the tumour, including its verges. In the end, the effects of different abnormal tissue shapes are investigated briefly as well. For solid mass tumors, 67.67% was successfully ablated with one lesion, while rim-enhancing tumors showed only 34.48% ablation and non-mass enhancement tumors exhibited 20.32% ablation, underscoring the need for multiple lesions and tailored treatment plans for more complex cases.
Copyright: © 2024 Rahpeima, Lin. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A holistic physics-informed neural network solution for precise destruction of breast tumors using focused ultrasound on a realistic breast model.Math Biosci Eng. 2024 Oct 18;21(10):7337-7372. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2024323. Math Biosci Eng. 2024. PMID: 39696866
-
Image-based 3D modeling and validation of radiofrequency interstitial tumor ablation using a tissue-mimicking breast phantom.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2012 Nov;7(6):941-8. doi: 10.1007/s11548-012-0769-3. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2012. PMID: 22688380
-
First clinical experience with a dedicated MRI-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound system for breast cancer ablation.Eur Radiol. 2016 Nov;26(11):4037-4046. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4222-9. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26852219 Free PMC article.
-
MR-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of breast cancer with a dedicated breast platform.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013 Apr;36(2):292-301. doi: 10.1007/s00270-012-0526-6. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23232856 Review.
-
High-intensity focused ultrasound in breast pathology: non-invasive treatment of benign and malignant lesions.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015 Mar;12(2):191-9. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2015.986096. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015. PMID: 25418428 Review.
References
-
- Bhowmik A, Repaka R, Mishra SC, Mitra K. Thermal assessment of ablation limit of subsurface tumor during focused ultrasound and laser heating. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications. 2016;8(1).
-
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics (2020) CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2020; 70 (1): 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Montienthong P, Rattanadecho P. Focused ultrasound ablation for the treatment of patients with localized deformed breast cancer: Computer simulation. Journal of Heat Transfer. 2019;141(10).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

