PfSPZ Vaccine induces focused humoral immune response in HIV positive and negative Tanzanian adults
- PMID: 39353279
- PMCID: PMC11464252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105364
PfSPZ Vaccine induces focused humoral immune response in HIV positive and negative Tanzanian adults
Abstract
Background: PfSPZ Vaccine, a promising pre-erythrocytic stage malaria vaccine candidate based on whole, radiation-attenuated Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) sporozoites (SPZ), has proven safe and effective in mediating sterile protection from malaria in malaria-naïve and exposed healthy adults. Vaccine-induced protection presumably depends on cellular responses to early parasite liver stages, but humoral immunity contributes.
Methods: On custom-made Pf protein microarrays, we profiled IgG and IgM responses to PfSPZ Vaccine and subsequent homologous controlled human malaria infection (CHMI) in 21 Tanzanian adults with (n = 12) or without (n = 9) HIV infection. Expression of the main identified immunogens in the pre-erythrocytic parasite stage was verified by immunofluorescence detection using freshly purified PfSPZ and an in vitro model of primary human hepatocytes.
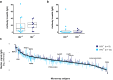
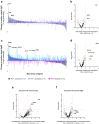
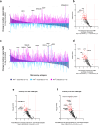
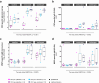
Findings: Independent of HIV infection status, immunisation induced focused IgG and IgM responses to circumsporozoite surface protein (PfCSP) and merozoite surface protein 5 (PfMSP5). We show that PfMSP5 is detectable on the surface and in the apical complex of PfSPZ.
Interpretation: Our data demonstrate that HIV infection does not affect the quantity of the total IgG and IgM antibody responses to PfCSP and PfMSP5 after immunization with PfSPZ Vaccine. PfMSP5 represents a highly immunogenic, so far underexplored, target for vaccine-induced antibodies in malaria pre-exposed volunteers.
Funding: This work was supported by the Equatorial Guinea Malaria Vaccine Initiative (EGMVI), the Clinical Trial Platform of the German Center for Infection Research (TTU 03.702), the Swiss Government Excellence Scholarships for Foreign Scholars and Artists (grant 2016.0056) and the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research doctoral program of the Tübingen University Hospital. The funders had no role in design, analysis, or reporting of this study.
Keywords: HIV; PfSPZ Vaccine; Plasmodium falciparum; Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein; Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein 5; Protein microarray.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Sanaria Inc. manufactured PfSPZ Vaccine and PfSPZ Challenge and was the sponsor of the clinical trial. YA, BKLS, TLR, TM, and SLH are salaried, full-time employees of Sanaria, and LWPC and PFB were full-time, salaried employees of Sanaria at the time the trial was conducted. All authors associated with Sanaria have potential conflicts of interest. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . 2013. World malaria report 2013.
-
- World Health Organization . 2023. World malaria report 2023.
-
- Phillips M.A., Burrows J.N., Manyando C., van Huijsduijnen R.H., Van Voorhis W.C., Wells T.N.C. Malaria. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3 - PubMed
-
- WHO Weekly epidemiological record, 2022, vol. 97, 09 [full issue] Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2022;97(09):61–80.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

