Endosomal fusion of pH-dependent enveloped viruses requires ion channel TRPM7
- PMID: 39353909
- PMCID: PMC11445543
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52773-w
Endosomal fusion of pH-dependent enveloped viruses requires ion channel TRPM7
Abstract
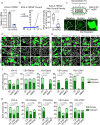
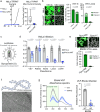
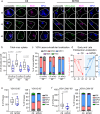
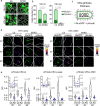
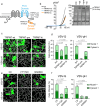
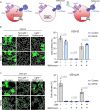
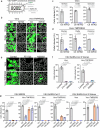
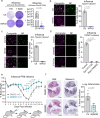
The majority of viruses classified as pandemic threats are enveloped viruses which enter the cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis and take advantage of endosomal acidification to activate their fusion machinery. Here we report that the endosomal fusion of low pH-requiring viruses is highly dependent on TRPM7, a widely expressed TRP channel that is located on the plasma membrane and in intracellular vesicles. Using several viral infection systems expressing the envelope glycoproteins of various viruses, we find that loss of TRPM7 protects cells from infection by Lassa, LCMV, Ebola, Influenza, MERS, SARS-CoV-1, and SARS-CoV-2. TRPM7 ion channel activity is intrinsically necessary to acidify virus-laden endosomes but is expendable for several other endosomal acidification pathways. We propose a model wherein TRPM7 ion channel activity provides a countercurrent of cations from endosomal lumen to cytosol necessary to sustain the pumping of protons into these virus-laden endosomes. This study demonstrates the possibility of developing a broad-spectrum, TRPM7-targeting antiviral drug to subvert the endosomal fusion of low pH-dependent enveloped viruses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.P.J.W. is a consultant for Thylacine Biosciences and receives support from Vir Biotechnology to study the properties of VSV-coronavirus chimeras unrelated to this project. J.S. receives support for research unrelated to this project from Icosavax. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI163019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI154598/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AG069264/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM108989/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 AI147394/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI163019/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 HL170961/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030557/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI030557/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 GM007055/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI154598/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM108989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL170961/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- AI155808/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- AI147394/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 GM007267/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007245/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI112844/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AI155808/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI030557/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112844/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

