Enfortumab Vedotin Following Platinum Chemotherapy and Avelumab Maintenance in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Retrospective Data from the ARON-2EV Study
- PMID: 39354179
- PMCID: PMC11557677
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-024-01099-0
Enfortumab Vedotin Following Platinum Chemotherapy and Avelumab Maintenance in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Retrospective Data from the ARON-2EV Study
Abstract
Background: Enfortumab vedotin (EV) has been approved for the treatment of patients with locally advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma (la/mUC) who previously received platinum-based chemotherapy followed by immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, the pivotal clinical trials did not include patients previously treated with avelumab maintenance therapy.
Objective: The aim of the present retrospective analysis was to assess the effectiveness of EV following avelumab in patients with mUC enrolled in the ARON-2EV study.
Patients and methods: The study included 182 patients with mUC treated with EV following avelumab maintenance. The primary objective was to assess clinical outcomes, including progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR), and duration of response (DoR). Statistical analysis involved Fisher exact test, Kaplan-Meier method, log-rank test, and univariate/multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models.
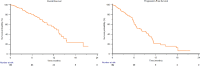
Results: Median OS and PFS were 12.7 (95% CI 10.2-14.1) and 7.9 (95% CI 6.4-9.9) months, respectively. Complete response (CR) was achieved in 5% and partial response (PR) in 34% of patients, with an ORR of 39%. The DoR in patients who achieved CR/PR was 10.9 months (95% CI 8.1-11.4). The incidence of grade ≥ 3 peripheral neuropathy and skin rash was 9%, followed by 8% of grade ≥ 3 diarrhea and 4% of grade ≥ 3 hyperglycemia.
Conclusions: The results of our large international retrospective study confirm the effectiveness of EV and endorse its use in the population of patients with mUC treated with EV following the frontline platinum-based chemotherapy and subsequent maintenance treatment with avelumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3068–77. - PubMed
-
- De Santis M, Bellmunt J, Mead G, Kerst JM, Leahy M, Maroto P, et al. Randomized phase II/III trial assessing gemcitabine/carboplatin and methotrexate/carboplatin/vinblastine in patients with advanced urothelial cancer who are unfit for cisplatin-based chemotherapy: EORTC study 30986. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:191–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Retz M, Siefker-Radtke A, Baron A, Necchi A, Bedke J, et al. Nivolumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum therapy (CheckMate 275): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:312–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

