CAR-redirected natural killer T cells demonstrate superior antitumor activity to CAR-T cells through multimodal CD1d-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 39354225
- PMCID: PMC12002392
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-024-00830-0
CAR-redirected natural killer T cells demonstrate superior antitumor activity to CAR-T cells through multimodal CD1d-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
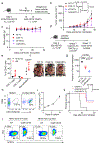
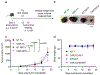
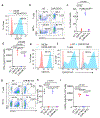
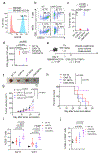
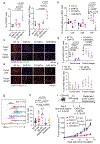
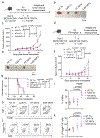
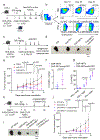
Human natural killer T (NKT) cells have been proposed as a promising cell platform for chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) therapy in solid tumors. Here we generated murine CAR-NKT cells and compared them with CAR-T cells in immune-competent mice. Both CAR-NKT cells and CAR-T cells showed similar antitumor effects in vitro, but CAR-NKT cells showed superior antitumor activity in vivo via CD1d-dependent immune responses in the tumor microenvironment. Specifically, we show that CAR-NKT cells eliminate CD1d-expressing M2-like macrophages. In addition, CAR-NKT cells promote epitope spreading and activation of endogenous T cell responses against tumor-associated neoantigens. Finally, we observed that CAR-NKT cells can co-express PD1 and TIM3 and show an exhaustion phenotype in a model of high tumor burden. PD1 blockade as well as vaccination augmented the antitumor activity of CAR-NKT cells. In summary, our results demonstrate the multimodal function of CAR-NKT cells in solid tumors, further supporting the rationale for developing CAR-NKT therapies in the clinic.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: G. Dotti serves in the SAB of Bellicum Pharmaceutical s.p.a., Catamaran Bio, Estella and Ouspecebio. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
Methods-only references
-
- Zhou X et al. YAP aggravates inflammatory bowel disease by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization and gut microbial homeostasis. Cell Reports 27, 1176–1189 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- IG2017-ID.20081/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- R01 CA262250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA262250/Division of Cancer Prevention, National Cancer Institute (NCI Division of Cancer Prevention)
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM138289/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35-GM138289/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 2019-ID.22737/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (Italian Association for Cancer Research)
- R01 CA243543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA243543/Division of Cancer Prevention, National Cancer Institute (NCI Division of Cancer Prevention)
- P30 DK034987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

