Comparison of laparoscopic hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a SEER population-based propensity score matching study
- PMID: 39354331
- PMCID: PMC11628577
- DOI: 10.1007/s13304-024-02016-w
Comparison of laparoscopic hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a SEER population-based propensity score matching study
Abstract
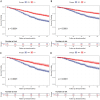
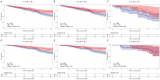
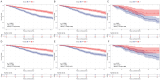
This study was designed to compare the efficacy of laparoscopic hepatectomy (LH) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in terms of their therapeutic effect on small hepatocellular carcinoma (SHCC). The SEER database was employed to integrate SHCC patients who had received treatment with either LH (n = 1132) or RFA (n = 797). The LH group (n = 623) and the RFA group (n = 623) were matched with 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) in order to reduce the possibility of selection bias. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression method were employed to ascertain the prognostic factors associated with overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS). Both before and after PSM, the 1, 3 and 5-years OS and DSS were significantly higher in the LH groups compared to the RFA group. Besides, for SHCC with tumor size ≤ 2cm (n = 418), even P values not reaching statistical significance, the survival curves were compatible with a superiority of LH over RFA for OS and DSS in overall (P = 0.054 and P = 0.077), primary SHCC (P = 0.110 and P = 0.058) and recurrent SHCC (P = 0.068 and P = 1.000) cohorts. In contrast, for SHCC with tumor size between 2 and 3 cm (n = 828), LH group always had a better OS and DSS in the all cohorts (all P < 0.05). In addition, higher AFP level, poor differentiation grade, recurrent tumor and treatment type were independent prognostic factors for OS, while poor differentiation grade, larger tumor size and treatment type were the independent prognostic factors for DSS (all P < 0.05). LH was associated with better OS and DSS than RFA in SHCC patients. Even in tumor size ≤ 2 cm, LH still should be the first choice as its long-term survival benefits.
Keywords: Laparoscopic hepatectomy; Prognosis; Propensity score matching; Radiofrequency ablation; Small hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. Ethical approval: Authors are responsible for all aspects of the work to ensure that questions about the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are properly investigated and resolved. Informed consent: Due to the retrospective type of study and the openness of the SEER database, informed consent was waived in this study.
Figures


References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca: Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249 - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Wang ZG, Fu SY et al (2016) Randomized clinical trial of chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Br J Surg 103(4):348–356 - PubMed
-
- Pinna AD, Yang T, Mazzaferro V et al (2018) Liver transplantation and hepatic resection can achieve cure for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 268(5):868–875 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

