Comparison between the standard method and the 30° curved tongue depressor-aided technique for insertion of a laryngeal mask airway: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39354369
- PMCID: PMC11445857
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-024-02741-0
Comparison between the standard method and the 30° curved tongue depressor-aided technique for insertion of a laryngeal mask airway: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
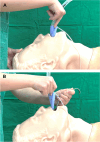
Background: Laryngeal mask airway (LMA) has been increasingly used for airway management; however, LMA insertion can be difficult and cause adverse effects. Therefore, the rapid, safe, and effective insertion of LMA is necessary. This study aimed to compare the efficacy of the standard method with that of the 30° curved tongue depressor-aided technique for LMA insertion to determine the superior technique.
Methods: This study included 154 patients aged 18-70 years (American Society of Anesthesiologists class I or II) scheduled for general anesthesia. The patients were randomly assigned to the standard LMA insertion group (Group C, n = 77) or the 30° curved tongue depressor-aided LMA insertion group (Group T, n = 77). The primary outcome evaluated was the first-attempt success rate. The secondary outcomes were the second-attempt success rate, insertion time, fiberoptic position grade, oropharyngeal leak pressure (OPLP), and adverse events.
Results: The first-attempt success rate was significantly higher in Group T than in Group C (97.40% vs. 88.31%, P = 0.029). The second-attempt success rate (P = 0.209), insertion time (P = 0.340), fiberoptic position grade (P = 0.872), and OPLP (P = 0.203) were slightly improved in Group T; however, there was no statistical significance. Bleeding events were reduced in Group T than in Group C (6.49% vs. 14.29%); however, there was no statistical significance. The incidence of sore throat symptoms was significantly reduced in Group T than in Group C (5.19% vs. 15.58%, P = 0.035).
Conclusions: The curved tongue depressor-aided technique significantly improved the first-attempt success rate of LMA insertion and reduced the incidence of sore throat symptoms.
Trial registration: KCT0004964; Registered at https://cris.nih.go.kr on April 27, 2020.
Keywords: Curved tongue depressor; First-attempt success rate; LMA insertion; Laryngeal mask airway; Standard technique.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ramachandran SK, Kumar AM. Supraglottic airway devices. Respir Care. 2014;59(6):920–32. - PubMed
-
- Yun MJ, Hwang JW, Park SH, Han SH, Park HP, Kim JH, et al. The 90° rotation technique improves the ease of insertion of the ProSeal™ laryngeal mask airway in children. Can J Anaesth. 2011;58(4):379–83. - PubMed
-
- Dhulkhed PV, Khyadi SV, Jamale PB, Dhulkhed VK. A prospective randomised clinical trial for the comparison of two techniques for the insertion of Proseal laryngeal mask airway in adults-index finger insertion technique versus 90° rotation technique. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2017;45(2):98–102. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

