Converse Flexoelectricity in van der Waals (vdW) Three-Dimensional Topological Insulator Nanoflakes
- PMID: 39355009
- PMCID: PMC11440597
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c05690
Converse Flexoelectricity in van der Waals (vdW) Three-Dimensional Topological Insulator Nanoflakes
Abstract
Low-dimensional van der Waals (vdW) three-dimensional (3D) topological insulators (TIs) have been overlooked, regarding their electromechanical properties. In this study, we experimentally investigate the electromechanical coupling of low-dimensional 3D TIs with a centrosymmetric crystal structure, where a binary compound, bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3), is taken as an example. Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) results of Bi2Se3 nanoflakes show that the material exhibits both out-of-plane and in-plane electromechanical responses. With careful analyses, the electromechanical responses are verified to arise from the converse flexoelectricity. The Bi2Se3 nanoflakes have a decreasing effective out-of-plane piezoelectric coefficient d 33 eff with the thickness increasing, with the d 33 eff value of ∼0.65 pm V-1 for the 37 nm-thick sample. The measured effective out-of-plane piezoelectric coefficient is mainly contributed by the flexoelectric coefficient, μ39, which is estimated to be approximately 0.13 nC m-1. The results can help to understand the flexoelectricity of low-dimensional vdW TIs with centrosymmetric crystal structures, which is crucial for the design of nanoelectromechanical devices and spintronics built by vdW TIs.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



 , denoted
as E3,3) of Ez inside the Bi2Se3 plate below
the tip apex, respectively, under
an voltage of 8 V. The tip shape is set to be consistent with the
one shown in (b). The thickness of the Bi2Se3 plate is 10 nm. (e, f) Line curves of E3 and E3,3 along the z direction.
, denoted
as E3,3) of Ez inside the Bi2Se3 plate below
the tip apex, respectively, under
an voltage of 8 V. The tip shape is set to be consistent with the
one shown in (b). The thickness of the Bi2Se3 plate is 10 nm. (e, f) Line curves of E3 and E3,3 along the z direction.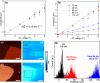

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
