Cellular and extracellular proteomic profiling of paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis myocardium
- PMID: 39355352
- PMCID: PMC11443424
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1398114
Cellular and extracellular proteomic profiling of paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis myocardium
Abstract
Aims: Patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS), low transvalvular flow (LF) and low gradient (LG) with normal ejection fraction (EF)-are referred to as paradoxical LF-LG AS (PLF-LG). PLF-LG patients develop more advanced heart failure symptoms and have a worse prognosis than patients with normal EF and high-gradient AS (NEF-HG). Despite its clinical relevance, the mechanisms underlying PLF-LG are still poorly understood.
Methods: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial biopsies of PLF-LG (n = 5) and NEF-HG patients (n = 6), obtained during transcatheter aortic valve implantation, were analyzed by LC-MS/MS after sequential extraction of cellular and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins using a three-step extraction method. Proteomic data are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD055391.
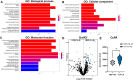
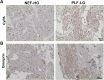
Results: 73 cellular proteins were differentially abundant between the 2 groups. Among these, a network of proteins related to muscle contraction and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (e.g., cTnI, FKBP1A and CACNA2D1) was found in PLF-LG. Extracellularly, upregulated proteins in PLF-LG were related to ATP synthesis and oxidative phosphorylation (e.g., ATP5PF, COX5B and UQCRB). Interestingly, we observed a 1.3-fold increase in cyclophilin A (CyPA), proinflammatory cytokine, in the extracellular extracts of PLF-LG AS patients (p < 0.05). Consistently, immunohistochemical analysis confirmed its extracellular localization in PLF-LG AS LV sections along with an increase in its receptor, CD147, compared to the NEF-HG AS patients. Levels of core ECM proteins, namely collagens and proteoglycans, were comparable between groups.
Conclusion: Our study pinpointed novel candidates and processes with potential relevance in the pathophysiology of PLF-LG. The role of CyPA in particular warrants further investigation.
Keywords: cellular and extracellular matrix proteomics; myocardial biopsies; normal ejection fraction high-gradient aortic stenosis; paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis; transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI).
© 2024 Elkenani, Barallobre-Barreiro, Schnelle, Mohamed, Beuthner, Jacob, Paul, Yin, Theofilatos, Fischer, Puls, Zeisberg, Shah, Mayr, Hasenfuß and Toischer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Puls M, Beuthner BE, Topci R, Vogelgesang A, Bleckmann A, Sitte M, et al. Impact of myocardial fibrosis on left ventricular remodelling, recovery, and outcome after transcatheter aortic valve implantation in different haemodynamic subtypes of severe aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J. (2020) 41:1903–14. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa033 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garbi M, MacCarthy P, Shah AM, Chambers JB. Classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis: a heart failure perspective. Struct Hear. (2018) 2:3–9. 10.1080/24748706.2017.1384876 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

