Adenosine triphosphate release inhibitors targeting pannexin1 improve recovery after spinal cord injury
- PMID: 39355370
- PMCID: PMC11439608
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.86.3.392
Adenosine triphosphate release inhibitors targeting pannexin1 improve recovery after spinal cord injury
Abstract
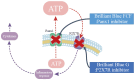
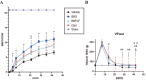
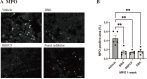
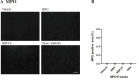
Traumatic spinal cord injury is characterized by immediate and irreversible tissue loss at the lesion site and secondary tissue damage. Secondary injuries should, in principle, be preventable, although no effective treatment options currently exist for patients with acute spinal cord injury. Traumatized tissues release excessive amounts of adenosine triphosphate and activate the P2X purinoceptor 7/pannexin1 complex, which is associated with secondary injury. We investigated the neuroprotective effects of the blue dye Brilliant Blue FCF, a selective inhibitor of P2X purinoceptor 7/pannexin1 that is approved for use as a food coloring, by comparing it with Brilliant Blue G, a P2X7 purinoceptor antagonist, and carbenoxolone, which attenuates P2X purinoceptor 7/pannexin1 function, in a rat spinal cord injury model. Brilliant Blue FCF administered early after spinal cord injury reduced spinal cord anatomical damage and improved motor recovery without apparent toxicity. Brilliant Blue G had the highest effect on this neurological recovery, with Brilliant Blue FCF and carbenoxolone having comparable improvement. Furthermore, Brilliant Blue FCF administration reduced local astrocytic and microglial activation and neutrophil infiltration, and no differences in these histological effects were observed between compounds. Thus, Brilliant Blue FCF protects spinal cord neurons after spinal cord injury and suppresses local inflammatory responses as well as Brilliant Blue G and carbenoxolone.
Keywords: adenosine triphosphate; purinergic P2X; receptors; spinal cord injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of methylprednisolone or naloxone in the treatment of acute spinal-cord injury. Results of the second national acute spinal cord injury study. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(20):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005173222001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
