Mendelian Randomization Studies in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 39355404
- PMCID: PMC11439750
- DOI: 10.12997/jla.2024.13.3.280
Mendelian Randomization Studies in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
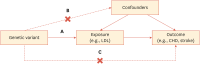
This review aimed to highlight the pivotal role of Mendelian randomization (MR) in advancing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) research-a field often hindered by the complexities and limitations of traditional studies. MR, which uses genetic variants as instrumental variables, provides a robust mechanism for inferring causality, offering insights untainted by the confounding factors and biases often prevalent in observational and randomized controlled trials. We explored the significant contributions of MR for elucidating the causal relationship between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASCVD, and analyzed its assumptions and methodological nuances. We discussed issues surrounding instrumental variable selection, pleiotropy, and ethical considerations, in an effort to offer a balanced and insightful analysis. We highlighted the promising integration of MR with emerging technologies and global data sharing, as well as its potential to drive personalized medicine. This review provided a concise yet comprehensive journey into MR's transformative impact on ASCVD research, offering a blend of current insights and challenges, in addition to future prospects. We aimed to serve a valuable resource for those seeking to navigate the intricate pathways of causality and intervention in ASCVD, to aid the development of enhanced understanding and targeted treatment strategies in the future.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Mendelian randomization analysis.
© 2024 The Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–ee528. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:56. - PubMed
-
- Kronzon I, Tunick PA. Aortic atherosclerotic disease and stroke. Circulation. 2006;114:63–75. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105:1135–1143. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources