Sinusoidal communication in chronic liver disease
- PMID: 39355871
- PMCID: PMC11791556
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0734
Sinusoidal communication in chronic liver disease
Abstract
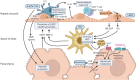
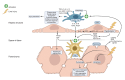
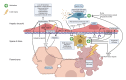
The liver sinusoid, mainly composed of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic macrophages and hepatic stellate cells, shapes the hepatic vasculature and is key to maintaining liver homeostasis and function. During chronic liver disease (CLD), the function of sinusoidal cells is impaired, being directly involved in the progression of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and main clinical complications including portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma. In addition to their roles in liver diseases pathobiology, sinusoidal cells' paracrine communication or cross-talk is being studied as a mechanism of disease but also as a remarkable target for treatment. The aim of this review is to gather current knowledge of intercellular signalling in the hepatic sinusoid during the progression of liver disease. We summarise studies developed in pre-clinical models of CLD, especially emphasizing those pathways characterized in human-based clinically relevant models. Finally, we describe pharmacological treatments targeting sinusoidal communication as promising options to treat CLD and its clinical complications.
Keywords: Chronic liver disease; Hepatic sinusoid; Hepatic stellate cells; Kupffer cells; Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Gracia-Sancho reports grants from Gilead Sciences, Novo Nordisk, GAT Therapeutics and Oncomatryx. In addition, he was offered lecture fees by Cell Pharma and BrudyLab, outside the submitted work. The rest of the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boyer TD, Wright TL, Manns MP. Zakim and Boyer’s hepatology e-book: a textbook of liver disease. Philadelphia: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2011. p. 1330.
-
- Augustin HG, Koh GY. Organotypic vasculature: from descriptive heterogeneity to functional pathophysiology. Science. 2017;357:eaal2379. - PubMed
-
- Gracia-Sancho J, Caparrós E, Fernández-Iglesias A, Francés R. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:411–431. - PubMed
-
- DeLeve LD, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, McCuskey RS. Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G757–G763. - PubMed

