SRSF6 modulates histone-chaperone HIRA splicing to orchestrate AR and E2F activity in prostate cancer
- PMID: 39356765
- PMCID: PMC11446284
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado8231
SRSF6 modulates histone-chaperone HIRA splicing to orchestrate AR and E2F activity in prostate cancer
Abstract
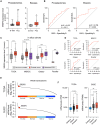
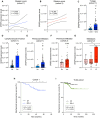
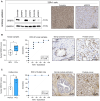
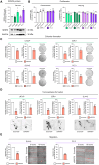
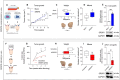
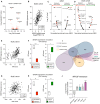
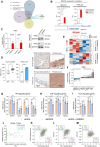
Despite novel therapeutic strategies, advanced-stage prostate cancer (PCa) remains highly lethal, pointing out the urgent need for effective therapeutic strategies. While dysregulation of the splicing process is considered a cancer hallmark, the role of certain splicing factors remains unknown in PCa. This study focuses on characterizing the levels and role of SRSF6 in this disease. Comprehensive analyses of SRSF6 alterations (copy number/mRNA/protein) were conducted across eight well-characterized PCa cohorts and the Hi-MYC transgenic model. SRSF6 was up-regulated in PCa samples, correlating with adverse clinical parameters. Functional assays, both in vitro (cell proliferation, migration, colony, and tumorsphere formation) and in vivo (xenograft tumors), demonstrated the impact of SRSF6 modulation on critical cancer hallmarks. Mechanistically, SRSF6 regulates the splicing pattern of the histone-chaperone HIRA, consequently affecting the activity of H3.3 in PCa and breast cancer cell models and disrupting pivotal oncogenic pathways (AR and E2F) in PCa cells. These findings underscore SRSF6 as a promising therapeutic target for PCa/advanced-stage PCa.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F., Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Westaby D., Fenor de La Maza M. L. D., Paschalis A., Jimenez-Vacas J. M., Welti J., de Bono J., Sharp A., A new old target: Androgen receptor signaling and advanced prostate cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 62, 131–153 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Paschalis A., Sharp A., Welti J. C., Neeb A., Raj G. V., Luo J., Plymate S. R., de Bono J. S., Alternative splicing in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 663–675 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Jiménez-Vacas J. M., Herrero-Aguayo V., Montero-Hidalgo A. J., Gómez-Gómez E., Fuentes-Fayos A. C., León-González A. J., Sáez-Martínez P., Alors-Pérez E., Pedraza-Arévalo S., González-Serrano T., Reyes O., Martínez-López A., Sánchez-Sánchez R., Ventura S., Yubero-Serrano E. M., Requena-Tapia M. J., Castaño J. P., Gahete M. D., Luque R. M., Dysregulation of the splicing machinery is directly associated to aggressiveness of prostate cancer. EBioMedicine 51, 102547 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

