Astrocyte-neuron crosstalk in neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 39357429
- PMCID: PMC12186082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2024.102925
Astrocyte-neuron crosstalk in neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
A fundamental feature shared across neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) is the disruption of synaptic circuit formation and homeostasis. During early life, non-neuronal cells called astrocytes tightly regulate the establishment of circuits by controlling formation, remodeling, stabilization, and maturation of synapses. Concurrently, astrocytes mature to meet the evolving needs of the developing brain. Bidirectional astrocyte-neuron communication synchronizes astrocyte maturation with synapse development. An emerging body of evidence supports the hypothesis that in NDDs, deficits in astrocyte-neuron communication underlie errors in synaptic circuit development. Here we will review and discuss these findings, with the aim of inspiring future research and guiding translational studies.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Cagla Eroglu reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. Cagla Eroglu reports financial support was provided by Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Gabrielle Sejourne reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
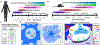
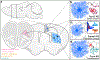
References
-
- Qian X, et al. , Timing of CNS cell generation: a programmed sequence of neuron and glial cell production from isolated murine cortical stem cells. Neuron, 2000. 28(1): p. 69–80. - PubMed
-
- Parenti I, et al. , Neurodevelopmental Disorders: From Genetics to Functional Pathways. Trends Neurosci, 2020. 43(8): p. 608–621. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. and American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5 Task Force., Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-5. 5th ed. 2013, Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association. xliv, 947 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

