GPCRs: emerging targets for novel T cell immune checkpoint therapy
- PMID: 39358616
- PMCID: PMC11447192
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-024-03801-7
GPCRs: emerging targets for novel T cell immune checkpoint therapy
Abstract
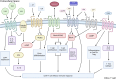
Although immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) has become the mainstay of treatment for advanced solid organ malignancies, success in revitalizing the host anticancer immune response remains limited. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a broad family of cell-surface proteins that have been regarded as main players in regulating the immune system, namely by mediating the activity of T lymphocytes. Among the most novel immunoregulatory GPCRs include GPR171, lysophosphatidic acid receptors (LPARs), GPR68, cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2), and prostaglandin E receptors, many of which have shown promise in mediating antitumor response via activation of cytotoxic T cells, inhibiting immunosuppressive lymphocytes, and facilitating immune cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment across multiple types of cancers. This paper reviews our current understanding of some of the most novel GPCRs-their expression patterns, evolving roles within the immune system and cancer, potential therapeutic applications, and perspective for future investigation.
Keywords: GPCRs; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; T cell; Tumor immunology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.D.S and Y.Z. are coinventors of a patent licensed to DynamiCure (managed by the University of Colorado) outside the submitted work. Y.Z. consults for DynamiCure Biotechnology. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ (2002) The B7-CD28 superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol 2(2):116–126 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

