Inflammatory proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease reduced by a GLP1 receptor agonist: a post hoc analysis of the EXSCEL randomized placebo controlled trial
- PMID: 39358806
- PMCID: PMC11448378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01573-x
Inflammatory proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease reduced by a GLP1 receptor agonist: a post hoc analysis of the EXSCEL randomized placebo controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are a viable option for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease (AD) but the mechanisms of this potential disease modifying action are unclear. We investigated the effects of once-weekly exenatide (EQW) on AD associated proteomic clusters.
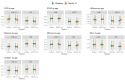
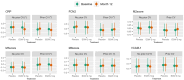
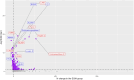
Methods: The Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering study compared the cardiovascular effects of EQW 2 mg with placebo in 13,752 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 4,979 proteins were measured (Somascan V0.4) on baseline and 1-year plasma samples of 3,973 participants. C-reactive protein (CRP), ficolin-2 (FCN2), plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), soluble vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (sVCAM1) and 4 protein clusters were tested in multivariable mixed models.
Results: EQW affected FCN2 (Cohen's d -0.019), PAI-1 (Cohen's d -0.033), sVCAM-1 (Cohen's d 0.035) and a cytokine-cytokine cluster (Cohen's d 0.037) significantly compared with placebo. These effects were sustained in individuals over the age of 65 but not in those under 65.
Conclusions: EQW treatment was associated with significant change in inflammatory proteins associated with AD.
Trial registration: EXSCEL is registered on ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01144338 on 10th of June 2010.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; Proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
IK received research support and honoraria from Novo Nordisk. He is a paid medical advisor for biotechnology (cfdx Ltd) and digital healthcare companies working in dementia (Five Lives SAS, Cognetivity, Mantrah Ltd). RJM received research support and honoraria from Abbott, American Regent, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Cytokinetics, Fast BioMedical, Gilead, Innolife, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Medable, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Relypsa, Respicardia, Roche, Rocket Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Verily, Vifor, Windtree Therapeutics, and Zoll. RRH reports personal fees from Anji Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Novartis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

