Cardiac Computed Tomography for Cardioembolic Stroke Evaluation in a Patient With a Mechanical Aortic Valve
- PMID: 39359973
- PMCID: PMC11442204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.102524
Cardiac Computed Tomography for Cardioembolic Stroke Evaluation in a Patient With a Mechanical Aortic Valve
Abstract
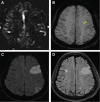
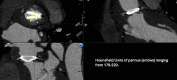
We present a case of cardioembolic stroke in a patient with a history of mechanical aortic valve who was compliant with anticoagulation medication. Cardiac computed tomography was used as an alternative, noninvasive means of evaluation for the cardioembolic source of stroke and identified subvalvular mobile pannus of the mechanical aortic valve.
Keywords: cardiac computed tomography; cardioembolic stroke; mechanical valve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- de Bruijn S.F.T.M., Agema W.R.P., Lammers G.J., et al. Transesophageal echocardiography is superior to transthoracic echocardiography in management of patients of any age with transient ischemic attack or stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(10):2531–2534. - PubMed
-
- Easton J.D., Saver J.L., Albers G.W., et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Stroke. 2009;40(6):2276–2293. - PubMed
-
- Otto C.M., Nishimura R.A., Bonow R.O., et al. 2020 ACC/AHA guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(4):e25–e197. - PubMed
-
- Bouzas-Mosquera A., Álvarez-García N. Orientation of bileaflet mechanical aortic valve prostheses for optimal evaluation by transthoracic echocardiography. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150(2):428–430. - PubMed
-
- Apfaltrer G., Lavra F., De Cecco C.N., et al. Predictive value of cardiac CTA, cardiac MRI, and transthoracic echocardiography for cardioembolic stroke recurrence. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;217(2):336–346. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

