Evaluation of Needles in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Pancreatic Cancer for Genetic Yield and Quality
- PMID: 39360054
- PMCID: PMC11445693
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.68431
Evaluation of Needles in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Pancreatic Cancer for Genetic Yield and Quality
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy (FNB) is the gold standard in tissue acquisition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). There is a paucity of evidence of the impact of needle type or size on the genetic yield and quality.
Methods: Patients 18 years and older with PDAC who underwent FNB were retrospectively identified from a single database from 2016 to 2021. Genetic quantity is measured in micrograms (µg) and quality defined by RNA or DNA integrity number (RIN and DIN). FNB needles examined were Acquire 22 gauge (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) and ProCore 22 and 20 gauges (Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA).
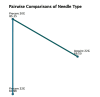
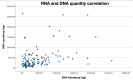
Results: Two hundred seventy-seven patients were identified. ProCore 20G needle procured higher RNA quantity (4125.8µg, IQR: 2003.8, 5954.8, p = 0.012) compared to ProCore 22G (2050µg IQR: 966.4, 3181.6) and Acquire 22G (2310.6µg, IQR: 1439.3, 4312). Median DNA quantity was 3340.5µg (Acquire 22G), 2610.4µg (ProCore 22G) and 3499.7µg (ProCore 20G) (p = 0.763). Median DIN was 7.3 (Acquire 22G and ProCore 22G) and 7.4 (ProCore 20G) (p = 0.449). Median RIN was 3.0 (Acquire 22G and ProCore 22G) and 2.7 (ProCore 20G) (p = 0.886).
Conclusion: ProCore 20G was associated with higher quantity of RNA. There were no differences in the quality acquired by different needles.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasound guided needle biopsy; genetic yield; needle size; needle type; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2024, Tiong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Monash Health issued approval 80025. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
22G Acquire vs. 20G Procore needle for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of pancreatic masses: a randomized study comparing histologic sample quantity and diagnostic accuracy.Endoscopy. 2020 Sep;52(9):747-753. doi: 10.1055/a-1160-5485. Epub 2020 May 14. Endoscopy. 2020. PMID: 32408361 Clinical Trial.
-
Histologic retrieval rate of a newly designed side-bevelled 20G needle for EUS-guided tissue acquisition of solid pancreatic lesions.United European Gastroenterol J. 2019 Feb;7(1):96-104. doi: 10.1177/2050640618804443. Epub 2018 Sep 30. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019. PMID: 30788121 Free PMC article.
-
IS THE NEW PROCORE 20G DOUBLE FORWARD-BEVEL NEEDLE CAPABLE TO OBTAIN BETTER HISTOLOGICAL SAMPLES BY ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND FOR DIAGNOSING SOLID PANCREATIC LESIONS?Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2021 Jan 25;33(4):e1554. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020200004e1554. eCollection 2021. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2021. PMID: 33503114 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comprehensive review of endoscopic ultrasound core biopsy needles.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2018 Feb;15(2):127-135. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2018.1425137. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2018. PMID: 29334842 Review.
-
Procore and flexible 19 gauge needle can replace trucut biopsy needle?Clin Endosc. 2013 Sep;46(5):503-5. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.5.503. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Clin Endosc. 2013. PMID: 24143312 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Puckett Y, Garfield K. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Pancreatic Cancer. - PubMed
-
- Assessment of HER-2 status in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: correlation of immunohistochemistry, quantitative real-time RT-PCR, and FISH with aneuploidy and survival. Saxby AJ, Nielsen A, Scarlett CJ, Clarkson A, Morey A, Gill A, Smith RC. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:1125–1134. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
