The intricate interplay between microglia and adult neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39360265
- PMCID: PMC11445663
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1456253
The intricate interplay between microglia and adult neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
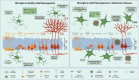
Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system, play a crucial role in regulating adult neurogenesis and contribute significantly to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Under physiological conditions, microglia support and modulate neurogenesis through the secretion of neurotrophic factors, phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, and synaptic pruning, thereby promoting the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of neural progenitor cells (NPCs). However, in AD, microglial function becomes dysregulated, leading to chronic neuroinflammation and impaired neurogenesis. This review explores the intricate interplay between microglia and adult neurogenesis in health and AD, synthesizing recent findings to provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of microglia-mediated regulation of adult neurogenesis. Furthermore, it highlights the potential of microglia-targeted therapies to modulate neurogenesis and offers insights into potential avenues for developing novel therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; adult neurogenesis; amyloid plaques; microglia; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2024 Früholz and Meyer-Luehmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

