Hand eczema and changes in the skin microbiome after 2 weeks of topical corticosteroid treatment
- PMID: 39360671
- PMCID: PMC12105447
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.20366
Hand eczema and changes in the skin microbiome after 2 weeks of topical corticosteroid treatment
Abstract
Background: More than 50% of patients with hand eczema (HE) are colonized with Staphylococcus aureus. Comprehensive knowledge of the skin microbiome and its changes in patients with HE may provide insights into future potential therapeutical targets.
Objective: To describe the skin microbiome in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic HE and assess its changes following treatment with topical corticosteroids (TCS).
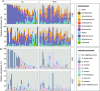
Methods: Bacterial samples were collected from lesional and nonlesional skin before and after 2 weeks of TCS treatment using ESwabs and analysed by 16S rRNA and tuf gene sequencing. Clinically, the disease severity was assessed by the Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI).
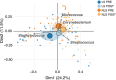
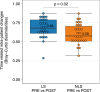
Results: A cohort of 31 patients with HE were included and followed up. Compared to nonlesional skin, lesional skin differed in overall bacterial community composition (p = 0.02), displayed higher relative abundance of Staphylococcus, in particular S. aureus (p = 0.01) and lower abundance of Micrococcus (p = 0.02). As disease severity improved with treatment, these microbial characteristics on lesional skin shifted towards that of nonlesional skin on the hands.
Conclusions: The bacterial skin microbiome was altered in lesions of HE and partly driven by S. aureus colonization, however, shifted towards nonlesional skin following treatment. Our results emphasize the future possibilities for anti-S. aureus treatment strategies.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Conflict of interest statement
LB Nørreslet, AC Ingham, PS Andersen, M Stegger, CG Mørtz, A Bregnhøj and SM Edslev have none to declare. T Agner: Involved with AbbVie, LEO Pharma A/S, Pfizer, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Galderma by grants, consulting fees, lectures. Advisory Board for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma A/S and Sanofi. CM Olesen: Employed as industrial postdoc at LEO Pharma and Bispebjerg Hospital. M Sommerlund: PI on Leo study DELTA2 og 3, not related to this study. Abbvie grant for participation in EADV congress 2022 and 2023. Leo‐Pharma advisory board for Delgocitinib 2024.
Figures
References
-
- Quaade AS, Simonsen AB, Halling AS, Thyssen JP, Johansen JD. Prevalence, incidence and severity of hand eczema in the general population – a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Contact Derm. 2021;84:361–374. - PubMed
-
- Meding B, Lantto R, Lindahl G, Wrangsjo K, Bengtsson B. Occupational skin disease in Sweden – a 12‐year follow‐up. Contact Derm. 2005;53(6):308–313. - PubMed
-
- Meding B, Wrangsjo K, Jarvholm B. Fifteen‐year follow‐up of hand eczema: persistence and consequences. Br J Dermatol. 2005;152(5):975–980. - PubMed
-
- Chapsa M, Rönsch H, Löwe T, Gunzer F, Beissert S, Bauer A. The role of bacterial colonisation in severity, symptoms and aetiology of hand eczema: the importance of Staphylococcus aureus and presence of commensal skin flora. Contact Derm. 2023;89(4):270–276. - PubMed
-
- Haslund P, Bangsgaard N, Jarlov JO, Skov L, Skov R, Agner T. Staphylococcus aureus and hand eczema severity. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161(4):772–777. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

