Overview of mechanism of electroacupuncture pretreatment for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- PMID: 39361504
- PMCID: PMC11448663
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14920
Overview of mechanism of electroacupuncture pretreatment for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
Abstract
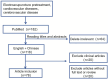
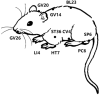
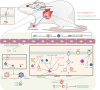
Cardio-cerebrovascular disease (CCVD) is a serious threat to huma strategy to prevent the occurrence and development of disease by giving electroacupuncture intervention before the disease occurs. EAP has been shown in many preclinical studies to relieve ischemic symptoms and improve damage from ischemia-reperfusion, with no comprehensive review of its mechanisms in cardiovascular disease yet. In this paper, we first systematically discussed the meridian and acupoint selection law of EAP for CCVD and focused on the progress of the mechanism of action of EAP for the prevention and treatment of CCVD. As a result, in preclinical studies, AMI and MCAO models are commonly used to simulate ischemic injury in CCVD, while MIRI and CI/RI models are used to simulate reperfusion injury caused by blood flow recovery after focal tissue ischemia. According to the meridian matching rules of EAP for CCVD, PC6 in the pericardial meridian is the most commonly used acupoint in cardiovascular diseases, while GV20 in the Du meridian is the most commonly used acupoint in cerebrovascular diseases. In terms of intervention parameters, EAP intervention generally lasts for 30 min, with acupuncture depths mostly between 1.5 and 5 mm, stimulation intensities mostly at 1 mA, and commonly used frequencies being low frequencies. In terms of molecular mechanisms, the key pathways of EAP in preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are partially similar. EAP can play a protective role in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases by promoting autophagy, regulating Ca2+ overload, and promoting vascular regeneration through anti-inflammatory reactions, antioxidant stress, and anti-apoptosis. Of course, both pathways involved have their corresponding specificities. When using EAP to prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases, it involves the metabolic pathway of glutamate, while when using EAP to prevent and treat cerebrovascular diseases, it involves the homeostasis of the blood-brain barrier and the release of neurotransmitters and nutritional factors. I hope these data can provide experimental basis and reference for the clinical promotion and application of EAP in CCVD treatment.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; cerebrovascular diseases; electroacupuncture pretreatment; mechanism; meridian.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced ferroptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Chin Med. 2025 May 9;20(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01114-0. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40346679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y. How to promote cardiovascular disease prevention. Electr J Clin Med Literature. 2019;6(24):198.
-
- Shijia Y. Constructing a three‐dimensional pattern of prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. doi:10.28415/n.cnki.njika.2023.003015 - DOI
-
- Jiajia T, Liya T, Xiaoying S, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on neurological function and expressions of VEGF and CD31 in the ischemic penumbra of rats with cerebral ischemia‐reperfusion injury. J Hunan Univ Chin Med. 2023;43(09):1679‐1684.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

