YY1 knockout in pro-B cells impairs lineage commitment, enabling unusual hematopoietic lineage plasticity
- PMID: 39362773
- PMCID: PMC11535188
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.351734.124
YY1 knockout in pro-B cells impairs lineage commitment, enabling unusual hematopoietic lineage plasticity
Abstract
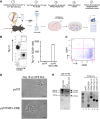
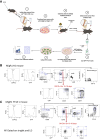
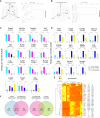
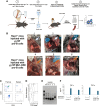
During B-cell development, cells progress through multiple developmental stages, with the pro-B-cell stage defining commitment to the B-cell lineage. YY1 is a ubiquitous transcription factor that is capable of both activation and repression functions. We found here that knockout of YY1 at the pro-B-cell stage eliminates B lineage commitment. YY1 knockout pro-B cells can generate T lineage cells in vitro using the OP9-DL4 feeder system and in vivo after injection into sublethally irradiated Rag1-/- mice. These T lineage-like cells lose their B lineage transcript profile and gain a T-cell lineage profile. Single-cell RNA-seq experiments showed that as YY1 knockout pro-B cells transition into T lineage cells in vitro, various cell clusters adopt transcript profiles representing a multiplicity of hematopoietic lineages, indicating unusual lineage plasticity. In addition, YY1 KO pro-B cells in vivo can give rise to other hematopoietic lineages in vivo. Evaluation of RNA-seq, scRNA-seq, ChIP-seq, and scATAC-seq data indicates that YY1 controls numerous chromatin-modifying proteins leading to increased accessibility of alternative lineage genes in YY1 knockout pro-B cells. Given the ubiquitous nature of YY1 and its dual activation and repression functions, YY1 may regulate commitment in multiple cell lineages.
Keywords: B-cell development; YY1; alternative lineages; hematopoietic lineage plasticity; lineage commitment; scATAC-seq; scRNA-seq; transcription.
© 2024 Banerjee et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures




Update of
-
Unusual lineage plasticity revealed by YY1 knockout in pro-B cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 27:2024.03.22.586298. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.22.586298. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genes Dev. 2024 Oct 16;38(17-20):887-914. doi: 10.1101/gad.351734.124. PMID: 38586061 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P, Brevdo E, Chen Z, Citro C, Corrado GS, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, et al. 2016. Tensorflow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 10.48550/arXiv.1603.0446 - DOI
-
- Andrews S. 2010. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Babraham Bioinformatics, Babraham Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
