A scoping review of reporting gaps in FDA-approved AI medical devices
- PMID: 39362934
- PMCID: PMC11450195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01270-x
A scoping review of reporting gaps in FDA-approved AI medical devices
Abstract
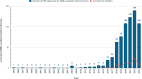
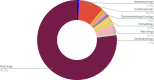
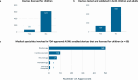
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI/ML) models in healthcare may exacerbate health biases. Regulatory oversight is critical in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of AI/ML devices in clinical settings. We conducted a scoping review on the 692 FDA-approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices approved from 1995-2023 to examine transparency, safety reporting, and sociodemographic representation. Only 3.6% of approvals reported race/ethnicity, 99.1% provided no socioeconomic data. 81.6% did not report the age of study subjects. Only 46.1% provided comprehensive detailed results of performance studies; only 1.9% included a link to a scientific publication with safety and efficacy data. Only 9.0% contained a prospective study for post-market surveillance. Despite the growing number of market-approved medical devices, our data shows that FDA reporting data remains inconsistent. Demographic and socioeconomic characteristics are underreported, exacerbating the risk of algorithmic bias and health disparity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML)-enabled medical devices. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artific... (2024).
-
- Center for Devices and Radiological Health. Medical Device Development Tools (MDDT). https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/medical-device-development-tools-mddt (2024).
-
- Ajraoui, S. & Ballester, B. R. Apple Watch AFib history feature makes medical device history. https://www.iqvia.com/blogs/2024/05/apple-watch-afib-history-feature-mak... (2024).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

