Selective inhibition of HDAC class IIA as therapeutic intervention for KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 39362994
- PMCID: PMC11450098
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06916-w
Selective inhibition of HDAC class IIA as therapeutic intervention for KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
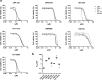
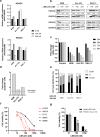
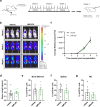
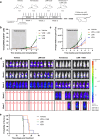
KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is characterized by deregulation of the epigenome and shows susceptibility towards histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition. Most broad-spectrum HDAC inhibitors simultaneously target multiple human HDAC isoforms. Consequently, they often induce toxicity and especially in combination with other therapeutic agents. Therefore, more specifically targeting HDAC isoforms may represent a safer therapeutic strategy. Here we show that shRNA-mediated knock-down of the class IIA HDAC isoforms HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC7 results in apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest in KMT2A-rearranged ALL cells. In concordance, the HDAC4/5 selective small molecule inhibitor LMK-235 effectively eradicates KMT2A-rearranged ALL cell lines as well as primary patient samples in vitro. However, using a xenograft mouse model of KMT2A-rearranged ALL we found that the maximum achievable dose of LMK-235 was insufficient to induce anti-leukemic effects in vivo. Similar results were obtained for the specific class IIA HDAC inhibitors MC1568 and TMP195. Finally, LMK-235 appeared to exert minimal anti-leukemic effects in vivo in combination with the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax, but not enough to prolong survival in treated mice. In conclusion, class IIA HDAC isoforms represent attractive therapeutic target in KMT2A-rearranged ALL, although clinical applications require the development of more stable and efficient specific HDAC inhibitors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Jansen, M. W. et al. Immunobiological diversity in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia is related to the occurrence and type of MLL gene rearrangement. Leukemia21, 633–641 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pieters, R. et al. A treatment protocol for infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Interfant-99): an observational study and a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet370, 240–250 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pieters, R. et al. Outcome of Infants Younger Than 1 Year With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated With the Interfant-06 Protocol: Results From an International Phase III Randomized Study. J. Clin. Oncol.37, 2246–2256 (2019). - PubMed
-
- van der Sluis, I. M. et al. Blinatumomab Added to Chemotherapy in Infant Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med388, 1572–1581 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

