Proteomic analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: pre- and postprandial comparisons
- PMID: 39363010
- PMCID: PMC11450010
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74228-4
Proteomic analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: pre- and postprandial comparisons
Abstract
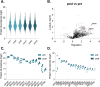
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are key in intercellular communication, carrying biomolecules like nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins. This study investigated postprandial characteristics and proteomic profiles of blood-derived EVs in healthy individuals. Twelve participants fasted overnight before baseline assessments. After consuming a controlled isocaloric meal, EVs were isolated for proteomic and flow cytometric analysis. Plasma triacylglyceride levels confirmed fasting completion, while protein concentrations in plasma and EVs were monitored for postprandial stability. Proteomic analysis identified upregulated proteins related to transport mechanisms and epithelial/endothelial functions postprandially, indicating potential roles in physiological responses to nutritional intake. Enrichment analyses revealed vesicle-related pathways and immune system processes. Flow cytometry showed increased expression of CD324 on CD9+CD63+CD81+ large extracellular vesicles postprandially, suggesting an epithelial origin. These findings offer valuable insights into postprandial EV dynamics and their potential physiological significance, highlighting the need for stringent fasting guidelines in EV studies to account for postprandial effects on EV composition and function.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Fasting; Liquid biopsy; Plasma; Postprandial; Proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

