Impact of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis for sexually transmitted infections on the gut microbiome and antimicrobial resistome
- PMID: 39363100
- PMCID: PMC11750720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03274-2
Impact of doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis for sexually transmitted infections on the gut microbiome and antimicrobial resistome
Abstract
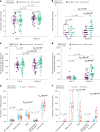
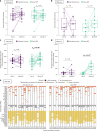
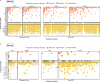
Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP) reduces bacterial sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men and transgender women. Although poised for widespread clinical implementation, the impact of doxy-PEP on antimicrobial resistance remains a primary concern as its effects on the gut microbiome and resistome, or the antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) present in the gut microbiome, are unknown. To investigate these effects, we studied participants from the DoxyPEP trial, a randomized clinical trial comparing doxy-PEP use, a one-time doxycycline 200-mg dose taken after condomless sex (DP arm, n = 100), to standard of care (SOC arm, n = 50) among men who have sex with men and transgender women. From self-collected rectal swabs at enrollment (day-0) and after 6 months (month-6), we performed metagenomic DNA sequencing (DNA-seq) or metatranscriptomic RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). DNA-seq data were analyzable from 127 samples derived from 89 participants, and RNA-seq data were analyzable from 86 samples derived from 70 participants. We compared the bacterial microbiome and resistome between the two study arms and over time. The median number of doxycycline doses taken since enrollment by participants with DNA-seq data was zero (interquartile range (IQR): 0-7 doses) for the SOC arm and 42 (IQR: 27-64 doses) for the DP arm. Tetracycline ARGs were detected in all day-0 DNA-seq samples and in 85% of day-0 RNA-seq samples. The proportional mass of tetracycline ARGs in the resistome increased between day-0 and month-6 in DP participants from 46% to 51% in the metagenome (P = 2.3 × 10-2) and from 4% to 15% in the metatranscriptome (P = 4.5 × 10-6), but no statistically significant increases in other ARG classes were observed. Exposure to a higher number of doxycycline doses correlated with proportional enrichment of tetracycline ARGs in the metagenome (Spearman's ρ = 0.23, P = 9.0 × 10-3) and metatranscriptome (Spearman's ρ = 0.55, P = 3.7 × 10-8). Bacterial microbiome alpha diversity, beta diversity and total bacterial mass did not differ between day-0 and month-6 samples from DP participants when assessed by either DNA-seq or RNA-seq. In an abundance-based correlation analysis, we observed an increase over time in the strength of the correlation between tetracycline ARGs and specific bacterial taxa, including some common human pathogens. In sum, doxy-PEP use over a 6-month period was associated with an increase in the proportion of tetracycline ARGs comprising the gut resistome and an increase in the expression of tetracycline ARGs. At 6 months of doxy-PEP use, no residual differences were observed in alpha and beta diversity or taxonomic composition of the gut microbiome. As doxy-PEP is implemented as a public health strategy, further studies and population-level surveillance of doxycycline-resistant pathogens are needed to understand the implications of these findings. ClinicalTrials.gov registration number: NCT03980223 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Mayne Pharmaceuticals donated doxycycline hyclate to the study, and Cepheid and Hologic provided reagents and STI diagnostic assays. Several authors have served as scientific advisors: to Merck (C. Celum and D.D.), to Gilead Sciences (C. Celum), to GlaxoSmithKline (C. Celum) and to Vir Biotechnology (A.L.). The other authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures







Update of
-
Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis for sexually transmitted infections impacts the gut antimicrobial resistome.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 17:rs.3.rs-4243341. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4243341/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Med. 2025 Jan;31(1):207-217. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03274-2. PMID: 38699315 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Molina, J.-M. et al. Post-exposure prophylaxis with doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men: an open-label randomised substudy of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. Lancet Infect. Dis.18, 308–317 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for the Use of Doxycycline Post-Exposure Prophylaxis for Bacterial STI Prevention.https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/guidelines-for-doxycycline.htm#print (2023).
-
- World Health Organization. WHO announces the development of the Consolidated Guidelines on STI prevention and care (2022–2023). https://www.who.int/news/item/18-05-2023-who-announces-the-development-o... (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

