Comparison of ustekinumab, infliximab and combination therapy in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis - a study protocol of a randomized, multicenter, head-to-head COMBO-UC trial
- PMID: 39364021
- PMCID: PMC11446819
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1458998
Comparison of ustekinumab, infliximab and combination therapy in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis - a study protocol of a randomized, multicenter, head-to-head COMBO-UC trial
Abstract
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease with a complex etiology that affects the large intestine. Characterized by chronic, bloody diarrhea, UC can lead to severe complications, including an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Despite advancements in conservative treatment, including biologics like anti-TNF agents and ustekinumab (UST), many patients do not achieve full remission. Dual targeted therapy (DTT) combining infliximab (IFX) and UST is a promising approach to improve treatment outcomes.
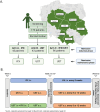
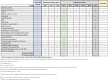
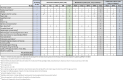
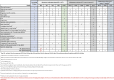
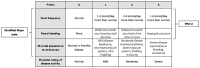
Methods: This prospective, randomized, multicenter, head-to-head controlled trial will evaluate the efficacy and safety of UST, IFX, and combination therapy (UST + IFX) in 172 patients with moderate to severe active UC across eight gastroenterology centers in Poland. The study includes a 14-16 week remission induction period followed by a 52-week maintenance phase. Patients will be randomly assigned to one of three treatment arms: IFX monotherapy, UST monotherapy, or IFX + UST combination therapy. Primary endpoint is clinical and endoscopic remission post-induction. Secondary endpoints include clinical response, biochemical remission, histological remission, and quality of life assessments using the Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Questionnaire and 36-Item Short Form Survey. Safety will be monitored through adverse event and serious adverse event reporting.
Discussion: This trial aims to determine whether combining IFX and UST can achieve higher remission rates and better long-term outcomes compared to monotherapy. The results could provide crucial insights into the optimal use of biologic agents in UC treatment, potentially establishing DTT as a standard therapy. The study's design, including extensive follow-up and robust endpoint measures, will contribute to understanding the therapeutic potential and safety profile of this combination therapy.
Keywords: dual biological therapy; inflammatory bowel diseases; infliximab; ulcerative colitis; ustekinumab.
Copyright © 2024 Talar-Wojnarowska, Fabisiak, Zatorski, Płoszka, Błaziak, Fendler, Rydzewska, Małecka-Wojciesko and Eder.
Conflict of interest statement
RT-W received lecture fees and/or travel grants from Abbvie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celtrion, Ferring, Janssen, Pfizer, Recordati, Sandoz, Takeda. AF received lecture fees and/or travel grants from Pro. Med.CS, Pfizer, Polpharma. HZ received lecture fees and/or travel grants from Nutricia, Fresenius Kabi, Ferring, Zentiva, Pro.Med.CS. EM-W received financial from Polpharma, Pfizer, Abbott, Mylan, Janssen, Celltrion, Varimed, Polpharma, Pro.Med.CS, Abbott, Mylan, Varimed, Takeda, Eli Lilly. PE received lecture fees and/or travel grants from Abbvie, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Ferring, Janssen, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Takeda, Sandoz, Pro.Med.CS, Sanofi. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
First-line biologics as a treatment for ulcerative colitis: a multicenter randomized control study.J Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr;60(4):430-441. doi: 10.1007/s00535-025-02216-0. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39883201 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Ustekinumab for Ulcerative Colitis: A Brazilian Multicentric Observational Study.Crohns Colitis 360. 2024 Apr 11;6(2):otae023. doi: 10.1093/crocol/otae023. eCollection 2024 Apr. Crohns Colitis 360. 2024. PMID: 38681979 Free PMC article.
-
Combination biologic therapy in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: Safety and efficacy over a minimum 12-month follow-up period.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024 Jul;79(1):54-61. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12179. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38477410
-
Ustekinumab in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Evolving Paradigms.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 6;13(5):1519. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051519. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of infliximab use in ulcerative colitis.Clin Ther. 2008 Feb;30(2):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.02.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18343261 Review.
Cited by
-
What is the optimal biological therapy for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 11;16:1602024. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1602024. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40717967 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 3;15(2):222. doi: 10.3390/biom15020222. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG4-related disease - focus on digestive system involvement.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1584107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584107. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40612937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eder P, Łodyga M, Gawron-Kiszka M, Dobrowolska A, Gonciarz M, Hartleb M, et al. . Guidelines for the management of ulcerative colitis. Recommendations of the polish Society of Gastroenterology and the polish National Consultant in gastroenterology. Gastroenterol Rev. (2023) 18:1–42. doi: 10.5114/pg.2023.125882 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

