Recent developments in intranasal drug delivery of nanomedicines for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
- PMID: 39364023
- PMCID: PMC11446881
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1463976
Recent developments in intranasal drug delivery of nanomedicines for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
Abstract
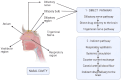
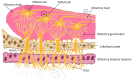
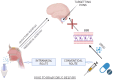
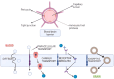
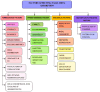
Neuropsychiatric disorders are multifaceted syndromes with confounding neurological explanations. It includes anxiety, depression, autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia, Tourette's syndrome, delirium, dementia, vascular cognitive impairment, and apathy etc. Globally, these disorders occupy 15% of all diseases. As per the WHO, India has one of the largest populations of people with mental illnesses worldwide. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) makes it extremely difficult to distribute medicine to target cells in the brain tissues. However, it is possible through novel advancements in nanotechnology, molecular biology, and neurosciences. One such cutting-edge delivery method, nose-to-brain (N2B) drug delivery using nanoformulation (NF), overcomes traditional drug formulation and delivery limitations. Later offers more controlled drug release, better bioavailability, improved patient acceptance, reduced biological interference, and circumvention of BBB. When medicines are delivered via the intranasal (IN) route, they enter the nasal cavity and go to the brain via connections between the olfactory and trigeminal nerves and the nasal mucosa in N2B. Delivering phytochemical, bioactive and synthetic NF is being investigated with the N2B delivery strategy. The mucociliary clearance, enzyme degradation, and drug translocations by efflux mechanisms are significant issues associated with N2B delivery. This review article discusses the types of neuropsychiatric disorders and their treatment with plant-derived as well as synthetic drug-loaded NFs administered via the IN-delivery system. In conclusion, this review provided a comprehensive and critical overview of the IN applicability of plant-derived NFs for psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: intranasal drug delivery; nanoformulation; nanomedicines; neuropsychiatric disorder; phytochemical and synthetic nanoformulation.
Copyright © 2024 Kisku, Nishad, Agrawal, Paliwal, Datusalia, Gupta, Singh, Dua and Sulakhiya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Convolutions in the rendition of nose to brain therapeutics from bench to bedside: Feats & fallacies.J Control Release. 2022 Jan;341:782-811. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.12.009. Epub 2021 Dec 11. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 34906605 Review.
-
Effective nose-to-brain drug delivery using a combination system targeting the olfactory region in monkeys.J Control Release. 2023 Jul;359:384-399. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.005. Epub 2023 Jun 16. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37315691
-
Nose-to-brain drug delivery: An update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs.J Control Release. 2018 Jul 10;281:139-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.05.011. Epub 2018 May 24. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29772289 Review.
-
Stimuli-responsive In situ gelling system for nose-to-brain drug delivery.J Control Release. 2020 Nov 10;327:235-265. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.044. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32739524 Review.
-
Nose-to-brain delivery of antipsychotics using nanotechnology: a review.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Jun;17(6):839-853. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1762563. Epub 2020 May 13. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32343186 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel and Emerging Treatments for Agitation in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 18;13(8):932. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13080932. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Nanocarrier Systems for Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 23;18(5):615. doi: 10.3390/ph18050615. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microplastics as Emerging Contaminants and Human Health: Exploring Functional Nutrition in Gastric-Colon-Brain Axis Cancer.Toxics. 2025 May 26;13(6):438. doi: 10.3390/toxics13060438. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40559911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nose to brain delivery of nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with rivastigmine and nilotinib for treating Alzheimer's disease: preparation, cell line study, and in vivo evaluation.Discov Nano. 2025 Jun 13;20(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04276-w. Discov Nano. 2025. PMID: 40512424 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals Modulate Biosynthesis and Function of Serotonin, Dopamine, and Norepinephrine for Treatment of Monoamine Neurotransmission-Related Psychiatric Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 23;26(7):2916. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072916. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Mental health and COVID-19: early evidence of the pandemic’s impact: scientific brief World Health Organization; (2022).
-
- Ritchie H, Ortiz-Ospina E, Beltekian D, Mathieu E, Hasell J, Macdonald B, et al. . (2020). Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Available at: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

