C-H Labeling with [18F]Fluoride: An Emerging Methodology in Radiochemistry
- PMID: 39364044
- PMCID: PMC11447958
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00997
C-H Labeling with [18F]Fluoride: An Emerging Methodology in Radiochemistry
Abstract
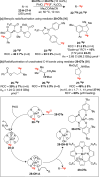
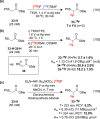
Fluorine-18 is the most routinely employed radioisotope for positron emission tomography, a dynamic nuclear imaging modality. The radiolabeling of C-H bonds is an attractive method for installing fluorine-18 into organic molecules since it can preclude the cumbersome prefunctionalization of requisite precursors. Although electrophilic "F+" reagents (e.g., [18F]F2) are effective for C-H radiolabeling, state-of-the-art methodologies predominantly leverage high molar activity nucleophilic [18F]fluoride sources (e.g., [18F]KF) with substantial (pre)clinical advantages. Reflecting this, multiple nucleophilic C-H radiolabeling techniques of high utility have been disclosed over the past decade. However, the adoption of (pre)clinical C-H radiolabeling has been slow, and PET imaging agents are still routinely prepared via methods that, despite a high level of practicality, are limited in scope (e.g., SNAr, SN2 radiofluorinations). By addressing the drawbacks inherent to these strategies, C-H radiofluorination and radiofluoroalkylation carry the potential to complement and supersede state-of-the-art labeling methods, facilitating the expedited production of PET agents used in disease staging and drug development. In this Outlook, we showcase recent C-H labeling developments with fluorine-18 and discuss the merits, potential, and barriers to adoption in (pre)clinical settings. In addition, we highlight trends, challenges, and directions in this emerging field of study.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

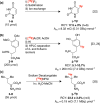




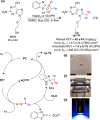

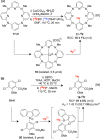
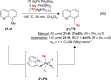

References
-
- Rinne J. O; Brooks D. J; Rossor M. N; Fox N. C; Bullock R.; Klunk W. E; Mathis C. A; Blennow K.; Barakos J.; Okello A. A; de LIano S. R. M.; Liu E.; Koller M.; Gregg K. M; Schenk D.; Black R.; Grundman M. 11C-PiB PET Assessment of Change in Fi Brillar Amyloid-β Load in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Treated with Bapineuzumab: A Phase 2, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Ascending-Dose Study. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 363–372. 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70043-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scott P. J. H.; Hockley B. G.. Radiochemical Syntheses: Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2012; Vol. 1, 10.1002/9781118140345. - DOI
-
- Packard A. B. SNMMI Leadership Update: Advocating for Our Field. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62 (3), 15N. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
