Transcriptomics-based anti-tuberculous mechanism of traditional Chinese polyherbal preparation NiuBeiXiaoHe intermediates
- PMID: 39364045
- PMCID: PMC11446850
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1415951
Transcriptomics-based anti-tuberculous mechanism of traditional Chinese polyherbal preparation NiuBeiXiaoHe intermediates
Abstract
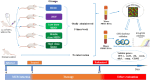
Background: Integrated traditional Chinese medicine and biomedicine is an effective method to treat tuberculosis (TB). In our previous research, traditional Chinese medicine preparation NiuBeiXiaoHe (NBXH) achieved obvious anti-TB effects in animal experiments and clinical practice. However, the action mechanism of NBXH has not been elucidated.
Method: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected to extract mRNA and differentially expressed (DE) genes were obtained using gene microarray technology. Finally, GEO databases and RT-qPCR were used to verify the results of expression profile.
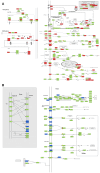
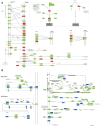
Result: After MTB infection, most upregulated DE genes in mice were immune-related genes, including cxcl9, camp, cfb, c4b, serpina3g, and ngp. Downregulated DE genes included lrrc74b, sult1d1, cxxc4, and grip2. After treatment with NBXH, especially high-dose NBXH, the abnormal gene expression was significantly corrected. Some DE genes have been confirmed in multiple GEO datasets or in pulmonary TB patients through RT-qPCR.
Conclusion: MTB infection led to extensive changes in host gene expression and mainly caused the host's anti-TB immune responses. The treatment using high-dose NBXH partially repaired the abnormal gene expression, further enhanced the anti-TB immunity included autophagy and NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and had a certain inhibitory effect on overactivated immune responses.
Keywords: Chinese traditional medicine; NiuBeiXiaoHe; mechanism of action; transcriptome; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Ma, Zhang, Wang, Li, Liang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative study on the antituberculous effect and mechanism of the traditional Chinese medicines NiuBeiXiaoHe extract and JieHeWan.Mil Med Res. 2021 Jun 2;8(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00324-5. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34074345 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Traditional Medicine NiuBeiXiaoHe (NBXH) Extracts Have the Function of Antituberculosis and Immune Recovery in BALB/c Mice.J Immunol Res. 2021 Jan 18;2021:6234560. doi: 10.1155/2021/6234560. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33575361 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine Niubeixiaohe in mouse tuberculosis models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 4;195:318-323. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.037. Epub 2016 Nov 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27884716
-
[Evolution of IGRA researches].Kekkaku. 2008 Sep;83(9):641-52. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18979999 Review. Japanese.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Experimental validation of cuproptosis-associated molecular signatures and their immunological implications in pulmonary tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1570992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1570992. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40808944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An H.-R., Wu X., Wang Z., Xu J., Zheng S., et al. (2013). The clinical characteristics of anti-tuberculosis drug induced liver injury in 2457 hospitalized patients with tuberculosis in China. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 7, 710–714. 10.5897/AJPP2013.2963 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

