The role of TRPV1 in chronic prostatitis: a review
- PMID: 39364048
- PMCID: PMC11446813
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1459683
The role of TRPV1 in chronic prostatitis: a review
Abstract
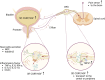
Chronic prostatitis is a prevalent male urinary system disorder characterized by pelvic discomfort or pain, bladder dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, and infertility. Pain and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) are the most common symptoms, significantly impacting patients' quality of life and driving them to seek medical attention. Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1) is a non-selective calcium ion-dependent cation channel in the TRPV channel family that is widely distributed in neural tissue and plays a role in signal transmission. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of the role of TRPV1 in chronic prostatitis. The discussion focuses on the connection between TRPV1 and prostatitis pain and LUTS, and highlights the potential for targeting this channel in the development of novel treatment strategies.
Keywords: TRPV1 channel; lower urinary tract symptoms; pain; prostatitis; therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2024 Jiang, Luo, Long and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Apostolidis A., Gonzales G. E., Fowler C. J. (2006). Effect of intravesical resiniferatoxin (RTX) on lower urinary tract symptoms, urodynamic parameters, and quality of life of patients with urodynamic increased bladder sensation. Eur. Urol. 50 (6), 1299–1305. 10.1016/j.eururo.2006.04.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

