Significance of research on natural products from marine-derived Aspergillus species as a source against pathogenic bacteria
- PMID: 39364162
- PMCID: PMC11446753
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1464135
Significance of research on natural products from marine-derived Aspergillus species as a source against pathogenic bacteria
Abstract
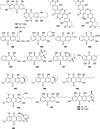
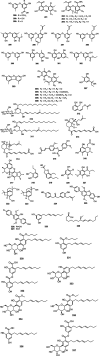
Bacterial infections pose a significant clinical burden on global health. The growing incidence of drug-resistant pathogens highlights the critical necessity to identify and isolate bioactive compounds from marine resources. Marine-derived fungi could provide novel lead compounds against pathogenic bacteria. Due to the particularity of the marine environment, Aspergillus species derived from marine sources have proven to be potent producers of bioactive secondary metabolites and have played a considerable role in advancing drug development. This study reviews the structural diversity and activities against pathogenic bacteria of secondary metabolites isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus species over the past 14 years (January 2010-June 2024), and 337 natural products (including 145 new compounds) were described. The structures were divided into five major categories-terpenoids, nitrogen-containing compounds, polyketides, steroids, and other classes. These antimicrobial metabolites will offer lead compounds to the development and innovation of antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: Aspergillus sp.; antibacterial activity; antimicrobial resistance; marine-derived; secondary metabolites.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Cai, Huang, Chen, Wang, Luo, Yang, Zhang, Nasihat, Chen, Huang and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer FC declared a past co-authorship with the author CZ to the handling editor.
Figures

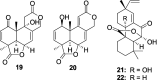
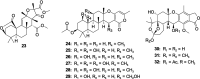










Similar articles
-
Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Fungi from China.Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2020;111:81-153. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-37865-3_2. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2020. PMID: 32114663
-
Marine Aspergillus: A Treasure Trove of Antimicrobial Compounds.Mar Drugs. 2023 Apr 28;21(5):277. doi: 10.3390/md21050277. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37233471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from a Thai Collection of Soil and Marine-Derived Fungi of the Genera Neosartorya and Aspergillus.Curr Drug Deliv. 2016;13(3):378-88. doi: 10.2174/1567201813666160303104641. Curr Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26935258 Review.
-
[New natural products from the marine-derived Aspergillus fungi-A review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016 Mar 4;56(3):331-62. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27382779 Review. Chinese.
-
Research Advances of Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids Isolated from Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp.Molecules. 2022 Oct 30;27(21):7376. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217376. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Activities of Aspergillus niger MF6: Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Cytotoxic Potential of Marine-Derived Fungus Metabolites.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Aug 25;82(10):473. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04457-x. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40850989
References
-
- Alahmari A. N., Hassoubah S. A., Alaidaroos B. A. (2022). Sponges-associated marine bacteria as sources of antimicrobial compounds. Novel. Res. Microbiol. J. 6, 1742–1767. doi: 10.21608/nrmj.2022.267424 - DOI
-
- Bao J., Li X. X., He F., Zhang X. Y., Zhu K. K., Tao H. R., et al. . (2020). Asperbutenolide a, an unusual aromatic butenolide dimer with diverse bioactivities from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCAU011. Tetrahedron Lett. 61:152193. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2020.152193 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

