NoFumo+: Mobile Health App to Quit Smoking Using Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
- PMID: 39364181
- PMCID: PMC11449556
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/8836672
NoFumo+: Mobile Health App to Quit Smoking Using Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Abstract
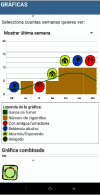
This paper describes the development and test of a smartphone application to quit smoking using cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The tool includes recommendations from US Clinical Practice Guidelines (USCPG), drawing on the potential of smartphones and complying with the health App (mHealth) assessment standards. The mHealth created, called NoFumo+, is structured by 4 weeks treatment, implements the USCPG 5A recommendations (ask, advise, assess, assist, and arrange) and incorporates a CBT. It also includes complementary information, monitoring of the smoking behavior, social support for users, proposals for alternative activities to smoking, and innovative gamification to encourage and reward adherence. To technical development, a multidisciplinary team was formed (healthcare, research, and software engineers) that made theoretical decisions on both technical issues and the incorporation of therapeutic techniques. The validation was carried out in two phases; the first in the laboratory by a group of experts in information and communication technologies and CBTs (n = 15) and the second, a field study with smokers (n = 10). The standards for the development of mHealth recommended by the Andalusian Healthcare Quality Agency and the App quality evaluation guidelines of the Catalonian ICT Foundation for Social Health were used as assessment protocols by the experts' panel and the smokers' group, respectively. Experts' assessment results were satisfactory and some improving changes were suggested, such as to add more gamification elements. The group of smokers rated the mHealth as 100% easy to use and effective for quit smoking and understandable by the 83.3%. They also found No Fumo + quite useful to have the information available at all times. The obtained evidence after a complete two-phased validation study, with experts and potential users, shows a mHealth with high quality and easy to use. Finally, investigation project registered in ClinicalTrials.gov with reference to this trial is registered with NCT045402004.
Copyright © 2024 Patricia García-Pazo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effective Behavioral Changes through a Digital mHealth App: Exploring the Impact of Hedonic Well-Being, Psychological Empowerment and Inspiration.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Jun 15;6(6):e10024. doi: 10.2196/10024. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018. PMID: 29907557 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Two Mobile Health Apps in the Context of Smoking Cessation: Qualitative Study of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Versus Non-CBT-Based Digital Solutions.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018 Apr 18;6(4):e98. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.9405. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018. PMID: 29669708 Free PMC article.
-
NoFumo+: A Clinical Trial of an mHealth for Smoking Cessation with Hospitalized Patients.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 6;18(19):10476. doi: 10.3390/ijerph181910476. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34639776 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional and Technical Aspects of Self-management mHealth Apps: Systematic App Search and Literature Review.JMIR Hum Factors. 2022 May 25;9(2):e29767. doi: 10.2196/29767. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022. PMID: 35612887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smartphone Apps for Smoking Cessation: Systematic Framework for App Review and Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 13;25:e45183. doi: 10.2196/45183. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37440305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abuse S. Substance abuse and mental health services administration. 2014. https://www.usa.gov/agencies/substance-abuse-and-mental-health-services-... .
-
- Plan Nacional Sobre Drogas. Informe 2021: Alcohol, Tabaco y Drogas ilegales en España. 2021. https://pnsd.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/sistemasInformacion/informesEs... .
-
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Europea de Salud en España (EESE) [Internet]. [National Institute of Statistics. European Health Survey in Spain (EESE) . 2021;2020
-
- World Health Organization. WHO launches new report on global trends in tobacco use. 2019. https://www.who.int/es/news-room/detail/19-12-2019-who-launches-new-repo... .
-
- Jiménez-Ruiz C. A., Fagerström K. O. El tabaquismo como enfermedad crónica. Visión global . España, Spain: Grupo Aula Médica S.L; 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

