Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants in Tehuledere District, Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 39364257
- PMCID: PMC11449547
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/3420352
Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants in Tehuledere District, Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
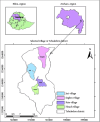
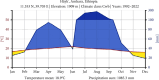
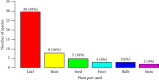
Medicinal plants have constituted a fundamental aspect of human health and wellness for millennia. The objective of this study was to document medicinal plants used to treat human and livestock ailments in the Tehuledere District. The data were collected using semistructured interviews, focus group discussions, and field observations with local informants. Preference ranking, direct matrix ranking, and informant consensus factor were used for data analysis. A total of 63 medicinal plant species belonging to 59 genera and 41 families were documented. The predominant families identified were Lamiaceae and Asteraceae, each containing 6 and 5 species, respectively. Of the recorded medicinal plants, 53 (80.95%) species were used for human ailments, whereas 12 (19.05%) species were used for animal health issues. Among the recorded medicinal plant species, shrubs constitute the highest number with 35% species. The most frequently used plant parts were leaves, accounting for 59% of remedies targeting human ailments. The administration of herbal treatments was primarily oral, aimed at addressing various diseases. The most significant threat to these medicinal plants was attributed to agricultural expansion, followed by the collection of firewood. The aim of documenting the use of medicinal plants in the treatment of diseases was to capture traditional practices, with species such as Eucalyptus globulus, Olea europaea subsp. cuspidata, and Lepidium sativum serving as the foundational basis for future pharmacological studies. It is imperative to prioritize the conservation of Laggera tomentosa and Urtica simensis to safeguard biodiversity and the cultural traditions associated with these endangered species. Engaging local communities in the management and conservation of plant resources, along with the preservation of their traditional knowledge, presents a cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Keywords: conservation; ethnobotany; herbal treatments; medicinal plants; threats.
Copyright © 2024 Worku Misganaw and Yalew Yiblet.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used to treat human and livestock ailments in Addi Arkay district, northwest Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025 May 9;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13002-025-00775-3. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025. PMID: 40346565 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnobotanical study of traditional medicinal plants used by the local people in Habru District, North Wollo Zone, Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2024 Jan 4;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13002-023-00644-x. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2024. PMID: 38178202 Free PMC article.
-
Traditionally used phytomedicines and their associated threats in Bita district, southwestern Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025 Feb 18;21(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13002-025-00753-9. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025. PMID: 39966803 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Plants Used to Treat Evil Eye Illness in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review.ScientificWorldJournal. 2025 May 19;2025:5498700. doi: 10.1155/tswj/5498700. eCollection 2025. ScientificWorldJournal. 2025. PMID: 40421322 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on ethnobotanico-pharmacological studies carried out in Morocco, from 1991 to 2015: Systematic review (part 1).J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113200. Epub 2020 Aug 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32750461
Cited by
-
Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used to treat human and livestock ailments in Addi Arkay district, northwest Ethiopia.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025 May 9;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13002-025-00775-3. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2025. PMID: 40346565 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

