Probiotics for preventing or treating COVID-19; a systematic review of research evidence and meta-analyses of efficacy for preventing death, severe disease, or disease progression
- PMID: 39364259
- PMCID: PMC11447443
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18526.1
Probiotics for preventing or treating COVID-19; a systematic review of research evidence and meta-analyses of efficacy for preventing death, severe disease, or disease progression
Abstract
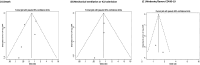
Background: COVID-19 variants threaten health globally. Despite improving vaccines and treatments, there is an urgent need for alternative strategies to prevent or reduce the severity of COVID-19. Potential strategies include probiotics, which are safe, inexpensive, globally available and have been studied previously in relation to respiratory infections. Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analyses of experimental, trial or observational research evidence evaluating probiotics compared with control groups for preventing or treating COVID-19. We searched PubMed, ProQuest, Google Scholar and Web of Science bibliographic databases for studies published until December 6, 2021. We then performed meta-analyses for outcomes reported consistently across studies. Outcomes reported inconsistently or not amenable to meta-analysis were compared descriptively. Results: We identified six eligible studies, which were all published in 2020 and 2021: one randomized controlled trial and five retrospective cohort studies. The only randomized controlled trial reported that groups that ingested probiotics compared with control groups that did not ingest probiotics did not differ significantly with respect to death, severe disease requiring admission to an intensive care unit or disease progression (all p>0.5). The five retrospective cohort studies reported various apparently beneficial and harmful COVID-19 outcome associations with probiotic ingestion. Meta-analyses revealed no significant associations between probiotic use and death, severe disease, or disease progression caused by COVID-19. Descriptive data revealed that probiotic ingestion was associated with a trend towards worsened duration of hospital stay, improvements in measures of respiratory condition and worsened disease duration. The evidence for these contradictory associations was weak because all studies were prone to bias and none were considered to be of high quality. Conclusions: Current evidence does not suggest that probiotics affect COVID-19 severity or mortality. However, additional higher quality studies need to be conducted to definitively determine if probiotics would be a useful adjunctive treatment for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Meta-analysis; Probiotics; SARS-CoV-2; Systematic Review.
Copyright: © 2022 Allen J et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics for preventing acute otitis media in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 18;6(6):CD012941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012941.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31210358 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 28;7(7):CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6:CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3. PMID: 34318930 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC): How to Prepare a Risk of Bias Table for Reviews That Include More than One Study Design. EPOC Resources for Review Authors.2017. Reference Source
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

