Optimal oxygen use in neonatal advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation-a literature review
- PMID: 39364342
- PMCID: PMC11449427
- DOI: 10.21037/pm-21-74
Optimal oxygen use in neonatal advanced cardiopulmonary resuscitation-a literature review
Abstract
Background and objectives: Oxygen (O2) use during neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) remains a subject of controversy. The inspired O2 concentration during neonatal CPR, that hastens return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), allows adequate cerebral and myocardial O2 delivery, and enhances survival to discharge, is not known. The optimal FiO2 during CPR should decrease incidence of hypoxia but also avoid hyperoxia, and ultimately lead to improved neurodevelopmental outcomes. Due to infrequent need for extensive resuscitation, and emergent circumstances surrounding neonatal CPR, conducting randomized clinical trials continues to be a challenge. The goal of this study was to review the evolution of oxygen use during neonatal CPR, the evidence from animal and clinical studies on oxygen use during neonatal CPR and after ROSC, the pertinent physiology including myocardial oxygen consumption and cerebral oxygen delivery during CPR, and outcomes following CPR in the DR and in the neonatal intensive care unit.
Methods: This narrative review is based on recent and historic English literature in PubMed and Google scholar over the past 35 years (January 1, 1985 - May 1, 2021).
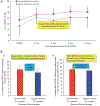
Key content and findings: Several studies in animal models have compared ventilation with different inspired O2 concentrations (mostly 21% and 100%) during chest compressions and after ROSC. These studies reported no difference in short-term outcomes, even with as low as 18% O2. However, in lamb models of cardiac arrest and CPR, 100% O2 during chest compressions is associated with better oxygen delivery to the brain compared to 21% O2. Abrupt weaning to 21% O2 following ROSC followed by titration to achieve preductal SpO2 of 85-95% minimizes systemic hyperoxia and oxidative stress compared to slow weaning from 100% O2 following ROSC.
Conclusions: Clinical research is needed to arrive at the best strategy for assessment of oxygenation and choice of FiO2 during neonatal CPR that lead to improved survival and outcomes. In this article, we have reviewed the literature on evidence behind O2 use during neonatal advanced CPR and after ROSC.
Keywords: Oxygen (O2); chest compressions (CC); hyperoxia; neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; neonatal resuscitation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Randomized Trial of 21% versus 100% Oxygen during Chest Compressions Followed by Gradual versus Abrupt Oxygen Titration after Return of Spontaneous Circulation in Neonatal Lambs.Children (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;10(3):575. doi: 10.3390/children10030575. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980132 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized trial of oxygen weaning strategies following chest compressions during neonatal resuscitation.Pediatr Res. 2021 Sep;90(3):540-548. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01551-1. Epub 2021 May 3. Pediatr Res. 2021. PMID: 33941864 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen requirement during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to effect return of spontaneous circulation.Resuscitation. 2009 Aug;80(8):951-5. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2009.05.001. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Resuscitation. 2009. PMID: 19520479
-
Optimal Chest Compression Rate and Compression to Ventilation Ratio in Delivery Room Resuscitation: Evidence from Newborn Piglets and Neonatal Manikins.Front Pediatr. 2017 Jan 23;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00003. eCollection 2017. Front Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28168185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Continuous compression with asynchronous ventilation improves CPR prognosis? A meta-analysis from human and animal studies.Am J Emerg Med. 2023 Feb;64:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2022.11.003. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Am J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 36435007 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Flow and Low-Flow Oxygen Delivery by Nasal Cannula Evaluated in Infant and Adult Airway Replicas.Respir Care. 2024 Mar 27;69(4):438-448. doi: 10.4187/respcare.11438. Respir Care. 2024. PMID: 38443141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barber CA, Wyckoff MH. Use and efficacy of endotracheal versus intravenous epinephrine during neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the delivery room. Pediatrics 2006;118:1028–34. - PubMed
-
- Soraisham AS, Lodha AK, Singhal N, et al. Neonatal outcomes following extensive cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the delivery room for infants born at less than 33 weeks gestational age. Resuscitation 2014;85:238–43. - PubMed
-
- Foglia EE, Weiner G, de Almeida MFB, et al. Duration of Resuscitation at Birth, Mortality, and Neurodevelopment: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2020;146:e20201449. - PubMed
-
- Kapadia VS, Chalak LF, DuPont TL, et al. Perinatal asphyxia with hyperoxemia within the first hour of life is associated with moderate to severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr 2013;163:949–54. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
