Intralesional gene expression profile of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and associated cytokines in Leishmania tropica- infected patients
- PMID: 39364404
- PMCID: PMC11446769
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436029
Intralesional gene expression profile of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and associated cytokines in Leishmania tropica- infected patients
Abstract
Background: The JAK-STAT signaling pathway is a central cascade of signal transduction for the myriad of cytokines in which dysregulation has been implicated in progression of inflammatory and infectious diseases. However, the involvement of this pathway in human cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) due to Leishmania (L.) tropica warrants further investigation.
Methods: This study sought to investigate differential gene expression of several cytokines and their associated jak-stat genes in the lesions of L. tropica-infected patients byquantitative Real-Time PCR. Further, the expression of five inhibitory immune checkpoint genes was evaluated.
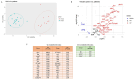
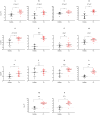
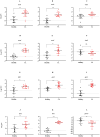
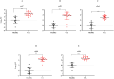
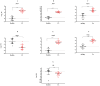
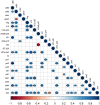
Results: Results showed that the gene expression levelsof both Th1 (ifng, il12, il23) and Th2 (il4, il10) types cytokines were increased in the lesion of studied patients. Further, elevated expression levels of il35, il21, il27 and il24 genes were detected in the lesions of CL patients. Notably, the expression of the majority of genes involved in JAK/STAT signaling pathway as well as checkpoint genes including pdl1, ctla4 and their corresponding receptors was increased.
Conclusion: Our finding revealed dysregulation of cytokines and related jak-stat genes in the lesion of CL patients. These results highlight the need for further exploration of the functional importance of these genes in the pathogenesis of, and immunity to, CL.
Keywords: JAK-STAT signaling pathway; Leishmania tropica; cutaneous leishmaniasis; cytokines; immune checkpoints.
Copyright © 2024 Hadifar, Masoudzadeh, Heydari, Mashayekhi Goyonlo, Kerachian, Daneshpazhooh, Sadeghnia, Tootoonchi, Erfanian Salim, Rafati and Harandi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Rasti S, Delavari M, Arani TST, Mousavi SGA. Epidemiological and clinical study on the cutaneous leishmaniasis in Aran and Bidgol, center of Iran. Int Arch Health Sci. (2018) 5:72–5. doi: 10.4103/iahs.iahs_26_18 - DOI
-
- Bamorovat M, Sharifi I, Agha Kuchak Afshari S, Ghasemi Nejad Almani P. Mutual role of patients and the healthcare system in the control of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Transboundary Emerging Dis. (2023) 2023:7814940. doi: 10.1155/2023/7814940 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

