Association of urinary albumin excretion with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a national prospective study
- PMID: 39364405
- PMCID: PMC11446789
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1412636
Association of urinary albumin excretion with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a national prospective study
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients suffering from chronic renal insufficiency tend to exhibit subtle manifestations at the beginning. Urine albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR) is a sensitive indicator for early assessment of renal function. However, it is unclear whether it serves as an independent risk factor influencing the prognosis of RA patients.
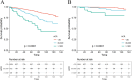
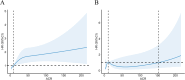
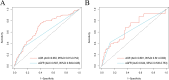
Methods: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data from 2009-2018 were included. Kaplan-Meier (K-M) curves were plotted to compare the cumulative survival probability of RA patients with different urinary albumin excretion. The association of ACR with mortality among RA patients was investigated with Cox regression model, restricted cubic spline (RCS) and stratified analyses. The prognostic efficacy of ACR and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
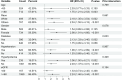
Results: The Cox regression model adjusted with covariates showed a 53% (HR 1.53, 95% CI 1.06-2.21) increase in all-cause mortality and a statistically non-significant increase in cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality in RA patients with microalbuminuria (30mg/g ≤ACR<300mg/g). ACR≥300mg/g was associated with an increase in all-cause mortality (HR 2.62, 95% CI 1.55-4.45) and CVD mortality (HR 5.67, 95% CI 1.96-16.39). RCS demonstrated a nonlinear correlation between ACR and all-cause mortality in RA patients with microalbuminuria. Subgroup analysis showed that CVD mortality was higher in RA patients with microalbuminuria characterized by the following features: female, other ethnicity, eGFR≥60 ml/min/1.73 m2, hypertension or hyperlipidemia. Compared with eGFR, ACR provided better prognostic efficacy than eGFR with higher values of the area under the curve (AUC) for all-cause mortality (AUC=0.683, 95% CI 0.613-0.754) and CVD mortality (AUC=0.681, 95% CI 0.541-0.820).
Conclusion: ACR is an independent risk factor affecting the prognosis of RA patients. The all-cause mortality was increased in RA patients with albuminuria. There was an upward trend in the CVD mortality of those with macroalbuminuria when ACR increased.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; mortality; rheumatoid arthritis; urinary albumin excretion; urine albumin to creatinine ratio.
Copyright © 2024 Bin, Shen, Wu, Fan, Zhang, Gao, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Borrelli S, Garofalo C, Gabbai FB, Chiodini P, Signoriello S, Paoletti E, et al. . Dipping status, ambulatory blood pressure control, cardiovascular disease, and kidney disease progression: A multicenter cohort study of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. (2023) 81:15–24.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.04.010 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

