Circulating extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers for pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 39364410
- PMCID: PMC11446868
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1374100
Circulating extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers for pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a serious complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with increased mortality. A prothrombotic state may contribute to pathogenesis of SLE-PAH. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are known to be associated with thrombosis. Here, we investigated circulating EVs and their associations with SLE-PAH.
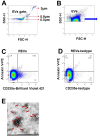
Methods: Eighteen SLE-PAH patients, 36 SLE-non-PAH patients, and 36 healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled. Flow cytometry was used to analyze circulating EVs from leukocytes (LEVs), red blood cells (REVs), platelets (PEVs), endothelial cells (EEVs), and Annexin V+ EVs with membrane phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure.
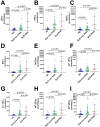
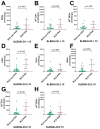
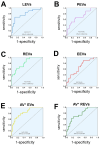
Results: Plasma levels of all EV subgroups were elevated in SLE patients with or without PAH compared to HCs. Furthermore, plasma Annexin V+ EVs, LEVs, PEVs, REVs, EEVs, and Annexin V+ REVs were significantly elevated in SLE-PAH patients compared to SLE-non-PAH patients. Additionally, PAH patients with moderate/high SLE showed a significant increase in LEVs, PEVs, REVs, Annexin V+ EVs, and Annexin V+ REVs compared to SLE-non-PAH patients. However, PAH patients with inactive/mild SLE only exhibited elevations in Annexin V+ EVs, REVs, and Annexin V+ REVs. In the SLE-PAH patients, EEVs were positively correlated with pulmonary arterial systolic pressure, while PEVs and EEVs were positively correlated with right ventricular diameter. Moreover, the receiver operating characteristic curve indicated that Annexin V+ EVs, LEVs, PEVs, REVs, EEVs and Annexin V+ REVs could predict the presence of PAH in SLE patients. Importantly, multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that circulating levels of LEVs or REVs, anti-nRNP antibody, and serositis were independent risk factors for PAH in SLE patients.
Discussion: Findings reveal that specific subgroups of circulating EVs contribute to the hypercoagulation state and the severity of SLE-PAH. Higher plasma levels of LEVs or REVs may serve as biomarkers for SLE-PAH.
Keywords: biomarker; extracellular vesicles; procoagulant; pulmonary arterial hypertension; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Qi, Liu, Wang, Zhang, Lyu, Sun, Du, Song, Hou, Guo, Wang, Liu and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yamin M, Faisal E, Putranto R, Shatri H. Major depressive disorder in a patient with systemic lupus erythematous, pulmonary hypertension, and hypercoagulation: A case report. Acta Med Indonesiana. (2022) 54:459–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

