Online eurythmy therapy for cancer-related fatigue: a prospective repeated-measures observational study exploring fatigue, stress, and mindfulness
- PMID: 39364432
- PMCID: PMC11447702
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2024.1472562
Online eurythmy therapy for cancer-related fatigue: a prospective repeated-measures observational study exploring fatigue, stress, and mindfulness
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer is a debilitating disease with an often chronic course. One of the most taxing and prevalent sequelae in this context is cancer-related fatigue (CRF) resulting from the disease and/or associated treatments. Over the last years mindfulness-based interventions such as eurythmy therapy (ERYT), a mindful-movement therapy from anthroposophic medicine, have emerged as promising adjunct therapies in oncology. This prospective study investigated an online implementation of ERYT for CRF using a single arm repeated-measures design based on two consecutive studies.
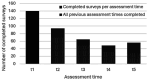
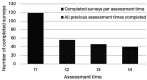
Method: Study 1 consisted of an initial assessment before, during, after, and at follow up of a 6-week online ERYT-based program in a mixed sample of N = 165 adults with or without cancer diagnosis. Study 2 involved a similar design with an adapted 8-week online ERYT-based program in a sample of N = 125 adults who had been diagnosed with cancer. Outcomes were assessed using the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, Perceived Stress Scale, Mindful Attention Awareness Scale, and Insomnia Severity Index (for Study 1 all, for Study 2 only the former three). We additionally performed an exploratory analysis regarding practice frequency and duration. Data were analyzed using Linear Mixed-Effect Models per outcome; ANOVA was used for practice times.
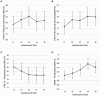
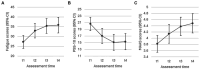
Results: For Study 1, mixed-effects model estimates showed no significant effect on fatigue, but pointed to significantly improved emotional and physical well-being, reduced stress, as well as increased mindfulness (mixed subjects). Functional and social well-being or sleep quality did not change significantly. Study 2 model estimates on the other hand showed significantly improved CRF in conjunction with the ERYT-based online intervention, as well as improved stress and mindfulness scores (cancer-diagnosed subjects).
Conclusion: Taken together, while our results should be interpreted with caution given the single-arm design and relatively high dropout, they suggest online ERYT may be associated with a reduction in fatigue for individuals diagnosed with cancer, an increase in mindfulness, and benefits for stress and certain well-being indicators. The online group format is advantageous in view of affordability and accessibility, the latter being particularly relevant for individuals who due to high symptom severity cannot leave their homes. Randomized-controlled studies will be needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: cancer; cancer-related fatigue; eurythmy therapy; fatigue; integrative medicine; mindful movement; mindfulness-based; online intervention.
Copyright © 2024 Timm, Ko, Hundhammer, Berlowitz and Wolf.
Conflict of interest statement
TH works as a therapist at the health provider Eurythmy4you but was not involved in the collection, handling, or analysis of data in this study, which was done independently by the scientific authors. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eurythmy therapy versus slow movement fitness in the treatment of fatigue in metastatic breast cancer patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jul 6;21(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04542-5. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32631427 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-based mindfulness: large-scale assessment of an online program on perceived stress and mindfulness.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1469316. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1469316. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39474093 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a combined multimodal-aerobic and multimodal intervention compared to standard aerobic treatment in breast cancer survivors with chronic cancer-related fatigue - results of a three-armed pragmatic trial in a comprehensive cohort design.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 2;17(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3142-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28253845 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Telephone interventions for symptom management in adults with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 2;6(6):CD007568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32483832 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67, 1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Bawa P. (2016). Retention in online courses: exploring issues and solutions—a literature review. SAGE Open 6:2158244015621777. doi: 10.1177/2158244015621777 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

