COPD associated pulmonary hypertension: A post hoc analysis of the PERFECT study
- PMID: 39364449
- PMCID: PMC11446833
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12430
COPD associated pulmonary hypertension: A post hoc analysis of the PERFECT study
Abstract
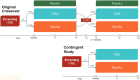
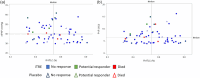
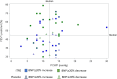
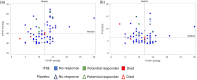
The PERFECT study, a randomized, controlled, double-blind study of inhaled treprostinil in patients with COPD and associated pulmonary hypertension (PH-COPD) was a negative trial that was terminated early. The reason(s) for the negative outcome remains uncertain. A post hoc analysis of data from the PERFECT study was undertaken to identify adverse responders and possibly potential responders. The goal was also to provide insight into phenotypes for possible inclusion and exclusion in future PH-COPD clinical trials. An adverse response on active treatment was seen in 36.4% (24/66) of the subjects compared to 27.6% (16/58) on placebo. There was no evidence to suggest that hyperinflation, bronchospasm, or occult heart failure played any role in the untoward outcomes of the study. The patients who died during the study all had baseline diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide ≤25% of predicted. Evidence of a potential response was seen in 10.6% (7/66) of the patients who received inhaled treprostinil. Patients who had evidence of a treatment response had a baseline mean pulmonary artery pressure of ≥40 mmHg and a forced expiratory volume in the first second of ≥40%. Change in N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide did not predict clinical response. This post hoc analysis provides information that may potentially enable improved selection of patients for future therapeutic trials in PH-COPD. These analyses are post hoc, observational, and exploratory. The thresholds defining the spectrum of responders are preliminary and may require further refinement and validation in future studies.
Keywords: chronic obstructive; double‐blind method; hypertension; pulmonary; pulmonary disease; treprostinil.
© 2024 The Author(s). Pulmonary Circulation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Steven D. Nathan, Aaron Waxman, Todd Bull and Victor Tapson are paid consultants for Lung Biotechnology and United Therapeutics. Victoria Lacasse, Heidi Bell, Prakash Sista, and Michael Di Marino are employees of United Therapeutics/Lung Biotechnology, the PERFECT study sponsor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD: PERFECT study results.Eur Respir J. 2024 Jun 6;63(6):2400172. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00172-2024. Print 2024 Jun. Eur Respir J. 2024. PMID: 38811045 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inhaled treprostinil and forced vital capacity in patients with interstitial lung disease and associated pulmonary hypertension: a post-hoc analysis of the INCREASE study.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Nov;9(11):1266-1274. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00165-X. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34214475 Clinical Trial.
-
Tiotropium bromide. A review of its use as maintenance therapy in patients with COPD.Treat Respir Med. 2004;3(4):247-68. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200403040-00005. Treat Respir Med. 2004. PMID: 15350163 Review.
-
Effect of lung deflation with indacaterol plus glycopyrronium on ventricular filling in patients with hyperinflation and COPD (CLAIM): a double-blind, randomised, crossover, placebo-controlled, single-centre trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2018 May;6(5):368-378. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30054-7. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Lancet Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29477448 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined aclidinium bromide and long-acting beta2-agonist for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 11;12(12):CD011594. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011594.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30536566 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cluster analysis identifies quantitative CT imaging-based subgroups in COPD subjects with pulmonary artery enlargement.Eur Respir J. 2025 Aug 8;66(2):2500038. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00038-2025. Print 2025 Aug. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40571325 Free PMC article.
-
Chest Computed Tomography to Improve Phenotyping in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2025 Feb;22(2):175-180. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202408-878PS. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2025. PMID: 39556097 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nathan SD, Argula R, Trivieri MG, Aziz S, Gay E, Medarov B, Parambil J, Raina A, Risbano MG, Thenappan T, Soto JS, Bell H, Lacasse V, Sista P, Di Marino M, Smart A, Hawkes B, Nelson E, Bull T, Tapson V, Waxman A. Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD: PERFECT study results. Eur Respir J. 2024;63(6):2400172. 10.1183/13993003.00172-2024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nathan SD, Deng C, King CS, DuBrock HM, Elwing J, Rajagopal S, Rischard F, Sahay S, Broderick M, Shen E, Smith P, Tapson VF, Waxman AB. Inhaled treprostinil dosage in pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease and its effects on clinical outcomes. Chest. 2023;163(2):398–406. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

