A Case of Transient Ventilation Difficulty Caused by the Occlusion of a Nasotracheal Intubation Tube Due to the Weight of the Tongue in a Patient With Morbid Obesity
- PMID: 39364478
- PMCID: PMC11449115
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.68488
A Case of Transient Ventilation Difficulty Caused by the Occlusion of a Nasotracheal Intubation Tube Due to the Weight of the Tongue in a Patient With Morbid Obesity
Abstract
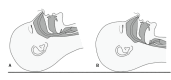
In patients with obesity, airway obstruction is more likely to occur because of the effects of gravity on the supine position and compression of the airway caused by the weight of soft tissues. This significantly increases the risk of apnea and hypoxemia. Therefore, careful airway monitoring and securing are essential after anesthesia induction and during postoperative recovery. Herein, we report a case of nasotracheal intubation tube obstruction caused by the weight of the tongue in a patient with morbid obesity during general anesthesia. This rare complication highlights the importance of careful airway monitoring and management in patients with obesity undergoing general anesthesia.
Keywords: airway management; airway obstruction; nasal intubation; obesity; tongue weight.
Copyright © 2024, Tachi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute airway obstruction requiring nasotracheal intubation following hypoglossal neuromonitoring: a case report.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 May 3;23(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02115-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37138238 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative management of a patient with Coffin-Lowry syndrome complicated by severe obesity: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(49):e9026. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009026. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29245289 Free PMC article.
-
Supraglottic jet oxygenation and ventilation assisted fiberoptic intubation in a paralyzed patient with morbid obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: a case report.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Mar 20;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0709-7. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 30894124 Free PMC article.
-
[Emergency anesthesia, airway management and ventilation in major trauma. Background and key messages of the interdisciplinary S3 guidelines for major trauma patients].Anaesthesist. 2011 Nov;60(11):1027-40. doi: 10.1007/s00101-011-1957-1. Anaesthesist. 2011. PMID: 22089890 Review. German.
-
Nasotracheal intubation for airway management during anesthesia.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021 Jul;16(3):232-247. doi: 10.17085/apm.21040. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 34352965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The impact of obesity on postoperative complications and short-term survival after liver transplantation. Tejedor-Tejada J, Garcia-Pajares F, Safadi R, et al. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;35:782–789. - PubMed
-
- Physiology of obesity and effects on lung function. Salome CM, King GG, Berend N. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2010;108:206–211. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources