Clinical Profile, Risk Factors, and Complications in Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 39364487
- PMCID: PMC11447432
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.68497
Clinical Profile, Risk Factors, and Complications in Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
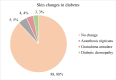
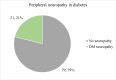
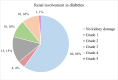
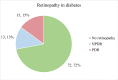
Background Young-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), defined as a diagnosis before the age of 45, is an increasingly common and aggressive form of diabetes. This population is at a heightened risk of developing complications earlier in life due to longer disease duration and often suboptimal glycemic control. Complications such as diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy are significant concerns, leading to reduced quality of life and increased morbidity. Objective To investigate the clinical profile and risk factors associated with complications of young-onset T2DM and to analyze the correlation between the age of onset and other parameters and the development of these complications. Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study on young-onset T2DM patients (<45 years) to investigate the prevalence and associated factors of diabetic complications. Variables analyzed included age, gender, BMI, waist-hip ratio, duration of diabetes, age at diagnosis, proteinuria, and glycosuria, along with biochemical markers such as HbA1C (glycated hemoglobin), serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and C-peptide levels. Results The average age of participants in our study was 34.76 ± 6.91 years. The mean BMI was 26.68 ± 3.35, with a mean cholesterol level of 169.84 ± 55.64 and a mean triglyceride level of 205.79 ± 67.49. The average HbA1c level was 9.82 ± 2.44. Diabetic neuropathy was found to increase significantly with advancing age (p < 0.001), longer duration of diabetes (p < 0.001), higher mean levels of HbA1C (p < 0.001), serum cholesterol (p = 0.006), and serum triglycerides (p = 0.010), as well as with lower levels of serum C-peptide (p = 0.025). The severity of kidney damage showed a significant association with older age (p = 0.049), longer diabetes duration (p < 0.01), elevated mean levels of HbA1C (p = 0.0002), and serum cholesterol (p = 0.0310). Diabetic retinopathy increased significantly with advancing age (p < 0.001), longer diabetes duration (p < 0.001), higher mean levels of HbA1C (p < 0.001), and serum triglycerides (p = 0.013). Conclusion Young-onset T2DM is associated with significant risks for neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy, particularly with increasing age and longer disease duration. Higher HbA1C, serum cholesterol, and triglyceride levels are prevalent among those with complications. These findings underscore the need for early intervention and targeted management strategies to mitigate complications in this high-risk population.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy (dn); diabetic peripheral neuropathy (dpn); diabetic retinopathy; obesity; young-onset diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2024, Dhadse et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee Human Research Lokmanya Tilak Municipal Medical College and General Hospital issued approval IEC/254/21. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microalbuminuria as the Tip of Iceberg in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Diabetic Complications.Cureus. 2023 Aug 9;15(8):e43190. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43190. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37692611 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Features and Microvascular Complications Risk Factors of Early-onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Med Sci. 2019 Oct;39(5):754-758. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2102-7. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Curr Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31612393
-
Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cureus. 2024 Mar 4;16(3):e55478. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55478. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38571859 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for the development and progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 22;2(2):CD013775. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013775.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36815723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes using Hemoglobin A1c: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic cutpoint based on microvascular complications.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Mar;58(3):279-300. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01606-5. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33141338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Nature. 2001;414:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Complications in young adults with early-onset type 2 diabetes: losing the relative protection of youth. Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2999–3005. - PubMed
-
- Prevalence of diabetes complications in adolescents with type 2 compared with type 1 diabetes. Eppens MC, Craig ME, Cusumano J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1300–1306. - PubMed
-
- Type 2 diabetes in younger adults: the emerging UK epidemic. Wilmot EG, Davies MJ, Yates T, Benhalima K, Lawrence IG, Khunti K. Postgrad Med J. 2010;86:711–718. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
