Genome-Wide Profiling of H3K27ac Identifies TDO2 as a Pivotal Therapeutic Target in Metabolic Associated Steatohepatitis Liver Disease
- PMID: 39364706
- PMCID: PMC11615751
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202404224
Genome-Wide Profiling of H3K27ac Identifies TDO2 as a Pivotal Therapeutic Target in Metabolic Associated Steatohepatitis Liver Disease
Abstract
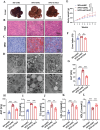
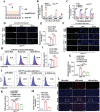
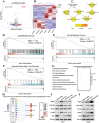
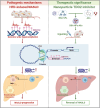
H3K27ac has been widely recognized as a representative epigenetic marker of active enhancer, while its regulatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) remain elusive. Here, a genome-wide comparative study on H3K27ac activities and transcriptome profiling in high fat diet (HFD)-induced MASLD model is performed. A significantly enhanced H3K27ac density with abundant alterations of regulatory transcriptome is observed in MASLD rats. Based on integrative analysis of ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq, TDO2 is identified as a critical contributor for abnormal lipid accumulation, transcriptionally activated by YY1-promoted H3K27ac. Furthermore, TDO2 depletion effectively protects against hepatic steatosis. In terms of mechanisms, TDO2 activates NF-κB pathway to promote macrophages M1 polarization, representing a crucial event in MASLD progression. A bovine serum albumin nanoparticle is fabricated to provide sustained release of Allopurinol (NPs-Allo) for TDO2 inhibition, possessing excellent biocompatibility and desired targeting capacity. Venous injection of NPs-Allo robustly alleviates HFD-induced metabolic disorders. This study reveals the pivotal role of TDO2 and its underlying mechanisms in pathogenesis of MASLD epigenetically and genetically. Targeting H3K27ac-TDO2-NF-κB axis may provide new insights into the pathogenesis of abnormal lipid accumulation and pave the way for developing novel strategies for MASLD prevention and treatment.
Keywords: H3K27ac; M1 polarization; MASLD; TDO2; YY1.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nuclear miR-204-3p mitigates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in mice.J Hepatol. 2024 Jun;80(6):834-845. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.01.029. Epub 2024 Feb 6. J Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38331323
-
Circular RNA RRM2 alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by targeting miR-142-5p to increase NRG1 expression.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):G485-G498. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00255.2023. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39259911
-
Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K27 acetylation featured fatty acid signalling in pancreatic beta cells in diet-induced obesity in mice.Diabetologia. 2018 Dec;61(12):2608-2620. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4735-7. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30284014
-
Vitamin D and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Novel Mechanistic Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4901. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094901. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-Induced Fatty Liver Disease (DIFLD): A Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical, Biochemical, and Histopathological Data for Mechanisms Identification and Consistency with Current Adverse Outcome Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5203. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105203. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Aging and its Rejuvenation.MedComm (2020). 2025 Sep 1;6(9):e70369. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70369. eCollection 2025 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40904701 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81702594 to H.Y. 82170484 to H.Q.Z. 82203866 to Y.Z. 82300661 to Y.L.Z/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2208085MH196 to B.C.Z/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province
- 2008085QH411 to Y.Z/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province
- 2308085QH246 to Y.L.Z/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province
- KJ2021A0205 to Y.L.Z/Natural Science Foundation of the Anhui Higher Education Institutions
- Scientific Research of BSKY from Anhui Medical University
- XJ201912 to Y.Z.: XJ201925 to Y.L.Z.
- 2020xkjT013toY.Z./Basic and Clinical Cooperative Research Promotion Program of Anhui Medical University
- 2022xkjT013toY.L.Z./Basic and Clinical Cooperative Research Promotion Program of Anhui Medical University
- 2019xkj010 to Y.Z/Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Medical University
- 2020xkj007 to Y.L.Z/Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Medical University
- 2023xkj002toY.S.T./Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Medical University
- 202210366024 to Y.L.Z/National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of China
- S202310366015 to Y.Z/National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
