Prevalence and influencing factors of malnutrition in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39364802
- PMCID: PMC11450603
- DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13610
Prevalence and influencing factors of malnutrition in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
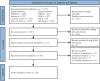
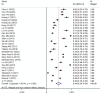
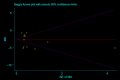
The prevalence of malnutrition in diabetic patients and its influencing factors remain poorly described. We aim to investigate the prevalence of malnutrition and the influencing factors in diabetic patients through meta-analysis. Utilizing search terms, such as diabetes, malnutrition, and prevalence, we systematically searched eight databases, including Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library, China Knowledge Resource Integrated Database (CNKI), Wanfang Database, Chinese Biomedical Database (CBM), and VIP Database, from inception to May 4, 2023. The search aimed to identify studies related to the prevalence of malnutrition and its influencing factors in adult patients with diabetes. Cohort studies, case-control studies, and cross-sectional studies that met the inclusion criteria were included in the analysis. Stata 16.0 software was used for meta-analysis. Quality of the evidence was assessed using Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE). The study protocol is registered with Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), CRD42023443649. A total of 46 studies were included, involving 18 062 patients with ages ranging from 18 to 95 years. The overall malnutrition prevalence was 33% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.25-0.40), compared with an at-risk prevalence of 44% (95% CI: 0.34-0.54). Sixteen factors associated with malnutrition in diabetic patients were identified. This meta-analysis provides insights into the prevalence of malnutrition and its risk factors in diabetic patients. Regular nutritional screening for patients with risk factors is essential for early detection and intervention.
Keywords: diabetes; influencing factors; malnutrition; meta‐analysis; prevalence.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Diabetes published by Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2008;26:77‐82. doi:10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77 - DOI
-
- López‐Valverde ME, Aragón‐Sánchez J, Víquez‐Molina G. Handgrip strength but not malnutrition according to global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria is a risk factor for mortality in hospitalized patients with ischemic diabetic foot ulcers. Adv Wound Care. 2023;12:127‐134. doi:10.1089/wound.2021.0109 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

