The importance of IgG glycosylation-What did we learn after analyzing over 100,000 individuals
- PMID: 39364834
- PMCID: PMC11659926
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.13407
The importance of IgG glycosylation-What did we learn after analyzing over 100,000 individuals
Abstract
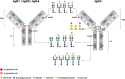
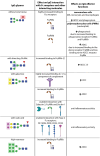
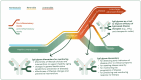
All four subclasses of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies have glycan structures attached to the protein part of the IgG molecules. Glycans linked to the Fc portion of IgG are found in all IgG antibodies, while about one-fifth of IgG antibodies in plasma also have glycans attached to the Fab portion of IgG. The IgG3 subclass is characterized by more complex glycosylation compared to other IgG subclasses. In this review, we discuss the significant influence that glycans exert on the structural and functional properties of IgG. We provide a comprehensive overview of how the composition of these glycans can affect IgG's effector functions by modulating its interactions with Fcγ receptors and other molecules such as the C1q component of complement, which in turn influence various immune responses triggered by IgG, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). In addition, the importance of glycans for the efficacy of therapeutics like monoclonal antibodies and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) therapy is discussed. Moreover, we offer insights into IgG glycosylation characteristics and roles derived from general population, disease-specific, and interventional studies. These studies indicate that IgG glycans are important biomarkers and functional effectors in health and disease.
Keywords: ADCC; CDC; Fcγ receptors; IVIg; IgG; glycosylation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Immunological Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
GL is founder and CEO and JK is employee of Genos, biotech company that is focusing on high‐throughput glycomics and has several patents in the field of glycan biomarkers. GL is a co‐founder and CSO of GlycanAge, biotech company that is developing and commercializing glycan biomarkers for biological age and disease prediction.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

