Glofitamab in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Results From a Phase I/II Study
- PMID: 39365960
- PMCID: PMC11771347
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02470
Glofitamab in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Results From a Phase I/II Study
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have a poor prognosis. The phase I/II NP30179 study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03075696) evaluated glofitamab monotherapy in patients with R/R B-cell lymphomas, with obinutuzumab pretreatment (Gpt) to mitigate the risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) with glofitamab. We present data for patients with R/R MCL.
Methods: Eligible patients with R/R MCL (at least one previous therapy) received Gpt (1,000 or 2,000 mg) 7 days before the first glofitamab dose (single dose or split over 2 days if required). Glofitamab step-up dosing was administered once a day on days 8 (2.5 mg) and 15 (10 mg) of cycle 1, with a target dose of 16 or 30 mg once every 3 weeks from cycle 2 day 1 onward, for 12 cycles. Efficacy end points included investigator-assessed complete response (CR) rate, overall response rate (ORR), and duration of CR.
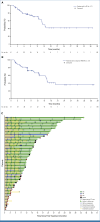
Results: Of 61 enrolled patients, 60 were evaluable for safety and efficacy. Patients had received a median of two previous therapies (range, 1-5). CR rate and ORR were 78.3% (95% CI, 65.8 to 87.9) and 85.0% (95% CI, 73.4 to 92.9), respectively. In patients who had received previous treatment with a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (n = 31), CR rate was 71.0% (95% CI, 52.0 to 85.8) and ORR was 74.2% (95% CI, 55.4 to 88.1). CRS after glofitamab administration occurred in 70.0% of patients, with a lower incidence in the 2,000 mg (63.6% [grade ≥2, 22.7%]) versus 1,000 mg (87.5%; grade ≥2, 62.5%) Gpt cohort. Four adverse events led to glofitamab withdrawal (all infections).
Conclusion: Fixed-duration glofitamab induced high CR rates in heavily pretreated patients with R/R MCL; the safety profile was manageable with appropriate support.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Wilson MR, Barrett A, Cheah CY, et al. How I manage mantle cell lymphoma: Indolent versus aggressive disease. Br J Haematol. 2023;201:185–198. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Doorduijn JK, Gine E, et al. Efficacy and safety of ibrutinib combined with standard first-line treatment or as substitute for autologous stem cell transplantation in younger patients with mantle cell lymphoma: Results from the randomized triangle trial by the European MCL Network. Blood. 2022;140:1–3. suppl 1.
-
- Cheah CY, Chihara D, Romaguera JE, et al. Patients with mantle cell lymphoma failing ibrutinib are unlikely to respond to salvage chemotherapy and have poor outcomes. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1175–1179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical